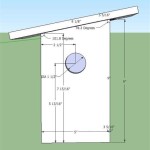
Essential Aspects of Green House Floor Plans
Designing a greenhouse requires careful consideration of various factors, including energy efficiency, space utilization, and plant well-being. Here are essential aspects to consider when creating a Green House Floor Plan:
1. Orientation and Sunlight Exposure
Proper orientation is crucial for maximizing sunlight exposure, which is vital for plant growth. Position the greenhouse facing south or southwest to maximize direct sunlight during the day. Also, ensure adequate spacing between the greenhouse and surrounding structures to minimize shading.
2. Layout and Space Allocation
Plan the greenhouse layout carefully to optimize space utilization. Divide the area into distinct zones for different plant types, ensuring sufficient space for growth and maintenance. Consider staging plants based on their size and light requirements to maximize efficiency.
3. Ventilation and Airflow
Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels inside the greenhouse. Incorporate passive ventilation methods, such as openable vents or ridge vents, to ensure air circulation and reduce the risk of condensation. Active ventilation systems, like fans or vents, may also be necessary.
4. Water Management
Greenhouse floors should facilitate proper water management. Design drainage systems to prevent waterlogging, which can damage plants and create a favorable environment for disease. Gutters and downspouts should effectively divert rainwater away from the structure.
5. Structural Considerations
The greenhouse frame should be designed to withstand wind and snow loads based on the specific location and climate conditions. Consider using durable materials like polycarbonate or fiberglass for the glazing. The floor should be level and well-supported to prevent uneven settling.
6. Pathways and Accessibility
Plan for clear pathways throughout the greenhouse to allow for easy access to plants, equipment, and maintenance tasks. Pathways should be wide enough for comfortable movement and accommodate the use of carts or machinery if necessary.
7. Utilities and Lighting
Ensure adequate electrical and plumbing infrastructure within the greenhouse. Electrical outlets should be conveniently located for lighting, heating, or cooling systems. Supplemental lighting may be necessary during low-light periods or for specific plant varieties.
8. Environmental Controls
Consider integrating environmental controls into the greenhouse floor plan. These systems can monitor temperature, humidity, and lighting, allowing for automated adjustments to optimize plant growth conditions. This can improve efficiency and reduce manual labor.
9. Energy Efficiency
Incorporate energy-efficient measures into the greenhouse design. Use insulated glazing, double- or triple-layer panels, and energy-saving lighting systems to reduce heating and cooling costs. Consider passive solar heating techniques, such as Trombe walls or clerestory windows, to minimize energy consumption.
10. Accessibility and Safety
Ensure the greenhouse design meets disability requirements and provides safe access for all users. Install ramps or elevators where necessary, and consider automated irrigation systems or other features to reduce the need for manual lifting.

Floor Plan Of The Greenhouse Scientific Diagram

Pin By Heba Imad On Greenhouse Plans Labs Plan

Floor Plan Greenhouse Home Deco Plans House 96539 Small

Facility Details Biological Sciences Greenhouse

Greenhouse

Ceres Schematic Design Bringing Your Commercial Greenhouse Facility From Idea To Reality Cans

The White Garden 2024 Review Greenhouse Border Herbidacious

Sample Htm Open Floor Plans With Discussion Of Your Many Options The Natural Home

Plan For Passive Solar Home And Garden Version 1 Byexample Com

Cross Section And Floor Plan Of The Closed Greenhouse System Set Up Scientific Diagram