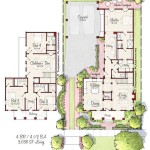
How To Design A Tiny House Floor Plan
Designing a functional and comfortable tiny house floor plan requires careful consideration of space optimization and lifestyle needs. This process involves several key steps, from initial brainstorming to finalizing dimensions and features.
Defining Needs and Lifestyle: The initial stage involves a thorough assessment of individual or family needs. Consider the number of occupants, essential amenities, and preferred lifestyle. Questions to consider include desired sleeping arrangements, cooking habits, work-from-home requirements, and storage needs. This information forms the foundation of the design process.
Setting a Realistic Budget: Establishing a budget early in the planning process helps guide material choices and design complexity. Researching the cost of materials, appliances, and professional services, if needed, provides a realistic framework for the project. Budget considerations impact both the size and features of the tiny house.
Determining the Tiny House Size and Dimensions: Based on the established needs and budget, determine the appropriate size and dimensions of the tiny house. Consider factors like mobility requirements if the house is intended to be on wheels. Local regulations regarding tiny house sizes should be researched and adhered to. Common tiny house dimensions range from 100 to 400 square feet.
Prioritizing Spaces and Functions: Prioritize the most important spaces and their functions. For example, if cooking is a priority, allocating ample space for a functional kitchen is essential. Similarly, those working from home might prioritize a dedicated workspace. This prioritization guides the layout and flow of the floor plan.
Creating Initial Sketches and Layouts: Begin with rough sketches and layouts to visualize the space. Explore different configurations and arrangements of rooms and furniture. Graph paper or online design tools can be utilized to create scaled drawings. This iterative process allows for experimentation and refinement.
Optimizing Vertical Space: Maximize vertical space through the incorporation of lofts, multi-functional furniture, and strategically placed storage solutions. Lofts can accommodate sleeping areas or additional storage, freeing up valuable floor space. Fold-down tables and convertible furniture further enhance space efficiency.
Considering Natural Light and Ventilation: Incorporate windows and skylights strategically to maximize natural light and ventilation. Well-placed windows can create a sense of spaciousness and reduce the need for artificial lighting. Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining air quality and preventing moisture buildup.
Selecting Appliances and Fixtures: Choose appliances and fixtures that are appropriately sized for a tiny house. Compact appliances designed for smaller spaces are readily available. Consider energy-efficient models to minimize utility costs. The selection of fixtures should align with the overall aesthetic and functionality of the design.
Refining the Floor Plan: Based on initial sketches and feedback, refine the floor plan, incorporating detailed measurements and specific features. Ensure that the layout allows for comfortable movement and accessibility. Consider traffic flow and the placement of doors and windows.
Incorporating Storage Solutions: Integrate clever storage solutions throughout the tiny house. Utilize under-bed storage, built-in shelving, and wall-mounted cabinets to maximize space utilization. Creative storage solutions help maintain a clutter-free and organized environment.
Utilizing Design Software (Optional): Consider using specialized design software to create a more detailed and professional floor plan. These programs offer 3D visualization and allow for precise measurements and adjustments. They can be particularly helpful for complex designs.
Reviewing and Finalizing the Design: Thoroughly review the final design, ensuring that it meets all identified needs and adheres to budget constraints. Double-check measurements and consider potential challenges. Consult with builders or other professionals if needed. Ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations.
Creating a Materials List: Once the design is finalized, create a comprehensive list of required materials. This list should include lumber, insulation, roofing materials, appliances, fixtures, and other necessary components. Accurate material estimations facilitate accurate budgeting and procurement.
Seeking Professional Advice (Optional): While not always necessary, consulting with architects, builders, or other professionals can provide valuable insights and ensure the structural integrity and safety of the design. Professional advice can be particularly beneficial for complex designs or those involving unconventional building techniques.

Tiny House Plan Examples

Family Tiny House Design Floor Plans Layout

Tiny House Design Floor Plans

Tiny House Floor Plans With Lower Level Beds Tinyhousedesign

Tiny House Floor Plans 32 Home On Wheels Design

Tiny House Plan Examples

Small Home Design Live 3d

Floor Plan 2 Bedroom Tiny House Interior

11 Best Tiny Houses With Genius Floorplans S Pics

How To Draw A Tiny House Floor Plan