House Extension Planning Consent
Extending one's home is a popular way to increase living space and add value to a property. However, navigating the regulations surrounding house extensions can be complex. Understanding planning consent requirements is crucial before embarking on any extension project. This article provides information regarding house extension planning consent in the UK, highlighting key aspects homeowners need to consider.
Planning permission is a legal requirement for many types of home extensions. It grants permission to carry out building work that materially alters a property. Whether planning permission is necessary depends on the size and type of extension being planned. Permitted development rights offer some flexibility, allowing specific extensions to be built without full planning permission. However, these rights are subject to limitations and conditions, and it's essential to understand the scope of these rights before commencing any work.
Permitted development rights vary depending on the type of property. Detached houses generally have more permitted development rights than semi-detached or terraced properties. Flats and maisonettes typically have the fewest permitted development rights. The location of the property also plays a role. Properties located in conservation areas, areas of outstanding natural beauty, or listed buildings are subject to stricter planning controls.
Before undertaking any construction, it's advisable to check whether permitted development rights apply to the planned extension. The Planning Portal website provides detailed guidance on permitted development rights for house extensions in England. Information for Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland can be found on their respective government websites. Checking with the local planning authority is always recommended to ensure compliance with specific local regulations.
Several factors influence whether planning permission will be required. The size of the proposed extension is a key determinant. Larger extensions are more likely to require planning permission than smaller ones. The location of the extension on the property also matters. Extensions to the front of a property are typically subject to more stringent rules than those to the rear. The height of the extension is another important factor. Taller extensions are more likely to require planning permission due to their potential impact on neighboring properties.
The materials used in the construction of the extension can also influence the need for planning permission. Using materials that are significantly different from the existing property might require permission. The impact of the extension on the surrounding area, including neighboring properties and the streetscape, is another important consideration. Extensions that significantly impact the amenity of neighboring properties, such as blocking light or overlooking windows, are more likely to require planning permission.
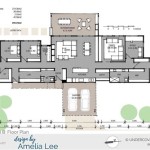
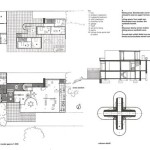
If planning permission is required, a formal application must be submitted to the local planning authority. The application process involves submitting detailed plans and drawings of the proposed extension, along with supporting documents. This includes a site plan, block plan, elevations, and floor plans. The application must also include information about the materials to be used and the impact of the extension on the surrounding area. A fee is typically payable upon submission of the application.
The local planning authority will assess the application against local planning policies and national guidance. They will consider factors such as the impact of the extension on the character of the area, the amenity of neighboring properties, and highway safety. The planning authority will consult with neighbors and other relevant stakeholders before making a decision. The decision-making process typically takes around eight weeks.
If planning permission is granted, it will be subject to conditions. These conditions might relate to the materials used, the height of the extension, or the timeframe for completion. It's essential to adhere to these conditions to avoid enforcement action. If planning permission is refused, there is a right of appeal. Appeals can be made to the Planning Inspectorate, an independent body that reviews planning decisions.
Engaging an architect or planning consultant can be beneficial throughout the process. They can provide expert advice on planning regulations, prepare the planning application, and manage the application process. Their expertise can significantly increase the chances of obtaining planning permission. Beginning any building work without the necessary planning permission can lead to significant complications. Enforcement action can result in fines and even the requirement to demolish the unauthorized extension.
Understanding the intricacies of planning permission is crucial for a successful house extension project. Thorough research, careful planning, and adherence to regulations will help ensure a smooth and compliant process. Consulting with professionals and utilizing online resources like the Planning Portal can provide valuable support throughout the project's lifecycle.

Do You Need Planning Permission For An Extension 2024

Do You Need Planning Permission For An Extension 2024

Do I Need Planning Permission For A Loft Conversion Or Extension Tomes Architects

Do I Need Planning Permission Www Prideroad Co

Q A How Will It Affect Families Planning An Extension

First Floor Two Y Extensions Do I Need Planning Permission

Homeowners Allowed To Do House Extensions Without Planning Permission Under New Rules Daily Mail

Government Relaxes Planning Rules Conservatories Orangeries Extensions

Do You Need Planning Permission For An Extension 2024

What Can I Build Without Planning Permission Darkin Architects