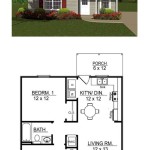
Sample Floor Plan of a House: Understanding Essential Elements and Design Considerations
A floor plan is a fundamental architectural diagram representing the arrangement of rooms and spaces within a building from a bird's-eye view. It is a crucial document for construction, renovation, and interior design projects, providing a visual guide for understanding the layout, dimensions, and relationships between different areas of a house. A well-crafted floor plan ensures efficient space utilization, optimal traffic flow, and a comfortable living environment. Understanding the elements and considerations involved in creating a sample floor plan is essential for both homeowners and professionals involved in the building process.
This article will explore the key components of a sample house floor plan, discuss various design considerations, and highlight the importance of accuracy and detail in its creation. Specific examples will be provided to illustrate different layout options and spatial arrangements, catering to a range of lifestyles and preferences. Furthermore, it will touch upon the tools and technologies used in floor plan design, including both traditional drafting methods and modern software applications.
Key Elements of a House Floor Plan
A comprehensive house floor plan includes several essential elements that work together to create a clear and informative representation of the building’s interior. These elements include walls, doors, windows, fixtures, and annotations, each playing a crucial role in defining the space and its functionality.
Walls: Walls are the primary structural elements defining the boundaries of rooms and spaces. They are typically represented by thick, solid lines on the floor plan. The thickness of the lines can indicate the type of wall, such as exterior walls, interior walls, or load-bearing walls. Dimensions are typically indicated to show the wall’s length and thickness. Proper wall placement is critical for structural integrity and efficient space utilization.
Doors: Doors provide access between rooms and to the exterior of the house. They are represented by a curved line indicating the direction of the door swing. The width of the door opening is also specified, influencing the accessibility and furniture placement within the adjacent spaces. Different types of doors, such as sliding doors, pocket doors, and bi-fold doors, can be used depending on space constraints and design preferences.
Windows: Windows are essential for natural light and ventilation. They are depicted as gaps in the walls, often with additional lines indicating the window type, such as single-hung, double-hung, or casement windows. The size and placement of windows are crucial considerations, influencing the amount of natural light entering the room and the overall energy efficiency of the house. The floor plan will also indicate windowsill height.
Fixtures: Fixtures include essential elements such as plumbing fixtures (toilets, sinks, showers, bathtubs), kitchen appliances (refrigerators, stoves, dishwashers), and other built-in features. These fixtures are typically drawn to scale, providing a realistic representation of their size and location. The placement of fixtures is critical for functionality and accessibility, particularly in bathrooms and kitchens.
Annotations: Annotations provide additional information about the rooms, spaces, and features depicted in the floor plan. These annotations include room names, dimensions, notes about materials, and any other relevant details. Accurate and clear annotations are essential for understanding the floor plan and ensuring that the construction or renovation process is carried out according to the design specifications.
Design Considerations for a House Floor Plan
Designing a house floor plan involves careful consideration of various factors, including lifestyle needs, space efficiency, traffic flow, accessibility, and aesthetics. The floor plan should reflect the homeowner's preferences and provide a comfortable and functional living environment. Several key design considerations are outlined below.
Lifestyle Needs: The floor plan should cater to the specific needs of the occupants. Families with young children may require a playroom or a large family room, while individuals who work from home may need a dedicated office space. Consider the number of bedrooms and bathrooms required, the need for storage space, and any specific hobbies or interests that require dedicated areas. The layout should optimize convenience and functionality for the occupants.
Space Efficiency: Efficient space utilization is crucial for maximizing the value of the house and creating a comfortable living environment. Avoid unnecessary hallways or wasted space. Consider open-concept layouts to create a sense of spaciousness and improve traffic flow. Multi-functional spaces can also be incorporated to optimize space utilization. For example, a guest room can double as a home office, or a dining area can be integrated into the living room.
Traffic Flow: The floor plan should facilitate smooth and efficient traffic flow throughout the house. Avoid creating bottlenecks or cramped areas that impede movement. Consider the natural paths that people will take through the house and design the layout accordingly. The placement of doors and hallways should be carefully considered to ensure easy access to all areas of the house. Consider how the inhabitants will move about the space, and design for ease of movement.
Accessibility: Accessibility is an important consideration, particularly for individuals with mobility issues or those planning to age in place. Ensure that doorways are wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs or walkers. Consider incorporating ramps or elevators for access to different levels of the house. Bathrooms and kitchens should be designed with accessible features such as grab bars and adjustable countertops. Wider hallways and larger turn radii should be considered for wheelchair access.
Aesthetics: The floor plan should be aesthetically pleasing and create a visually appealing environment. Consider the proportions of the rooms, the placement of windows, and the overall balance of the layout. Incorporate design elements that reflect the homeowner's personal style and preferences. The floor plan should also consider the relationship between the interior and exterior of the house, ensuring that the layout takes advantage of natural light and views.
Tools and Technologies for Floor Plan Design
Creating a floor plan can be achieved using various tools and technologies, ranging from traditional drafting methods to modern software applications. The choice of tool depends on the complexity of the project, the level of detail required, and the designer's preferences.
Traditional Drafting: Traditional drafting involves using tools such as pencils, rulers, compasses, and protractors to create floor plans manually. This method requires a high level of skill and precision but offers a hands-on approach to design. Traditional drafting is still used by some architects and designers, particularly for smaller projects or preliminary sketches. While time-consuming, it allows for detailed customization. It also requires physical storage of large-format drawings.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD software is a powerful tool for creating accurate and detailed floor plans. CAD programs allow designers to create 2D and 3D models of the house, incorporating precise measurements and specifications. CAD software also offers features such as automatic dimensioning, layering, and the ability to easily modify the design. Popular CAD programs include AutoCAD, Revit, and ArchiCAD. These programs often require specialized training to use effectively.
Floor Plan Software: Floor plan software offers a more user-friendly approach to design, with intuitive interfaces and drag-and-drop functionality. These programs are often geared towards homeowners and interior designers, allowing them to create floor plans quickly and easily. Floor plan software typically includes libraries of pre-designed furniture and fixtures, making it easy to visualize the space. Popular floor plan software includes Sweet Home 3D, Planner 5D, and RoomSketcher. These programs are often cloud-based or downloadable, making them easily accessible.
Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM is an advanced technology that goes beyond traditional CAD by creating a comprehensive digital representation of the building. BIM models include not only the geometry of the building but also information about the materials, systems, and components. BIM allows for better collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors, and can help to identify potential problems before construction begins. BIM software includes programs like Revit and ArchiCAD, which allow for complex 3D modeling and data management.
In summary, a well-designed floor plan is essential for creating a functional and comfortable living space. Understanding the key elements of a floor plan, considering various design factors, and utilizing appropriate tools and technologies are crucial for achieving a successful outcome.

12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

Ready To Use Sample Floor Plan Drawings Templates Easy Blue Print Floorplan Ezblueprint Com

Free Floorplan Template Inspirational Home Plans Sample House Floor Simple Plan Layout

Sample Floor Plan Image With The Specification Of Diffe Room Sizes Scientific Diagram

Ready To Use Sample Floor Plan Drawings Templates Easy Blue Print Floorplan Ezblueprint Com

12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

Home Floor Plans House Plan Drawings

Free Editable Open Floor Plans Edrawmax

Floor Plan Wikipedia

7 Modern House Plans Samples Home Small