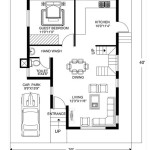
What Is a Front Elevation Plan?
A front elevation plan is a two-dimensional orthographic projection of a building's facade as viewed from a point directly in front of it. It represents the external appearance of the building's principal facade, showing its height, width, architectural features, and materials. This plan is a crucial component of architectural drawings, providing essential information for construction, permitting, and aesthetic visualization.
The term "elevation" in architectural parlance refers to a drawing that depicts a vertical plane. Unlike a floor plan, which shows the layout of rooms and internal features from a bird's-eye view, an elevation focuses on the exterior. The "front" designation indicates that this particular elevation represents the primary entrance or street-facing side of the building. However, buildings can have multiple elevations, including side, rear, and interior elevations, each providing a distinct view of the structure.
A front elevation plan is more than just a simple picture; it is a detailed technical drawing that accurately represents the building's proportions, materials, and design elements. It serves as a vital communication tool among architects, contractors, engineers, and clients, ensuring everyone has a clear understanding of the building's intended appearance.
The information contained within a front elevation plan is critical for a variety of purposes, from initial design conceptualization to final construction and landscaping. It provides a visual reference point for evaluating the design's aesthetic appeal while also serving as a practical guide for builders and other tradespeople.
Key Elements Depicted in a Front Elevation Plan
A comprehensive front elevation plan incorporates several key elements that are essential for understanding the building's design and ensuring accurate construction:
Architectural Features: This includes the depiction of windows, doors, balconies, porches, roofs, and any other prominent design features. The plan shows the size, shape, and placement of these elements, providing a clear understanding of their contribution to the overall design.
Materials: The materials used for the building's facade are indicated, either through notations or graphic representations. This includes specifying the type of brick, siding, stone, or other cladding materials, as well as the materials used for windows, doors, and trim. The plan may also specify the color and texture of these materials.
Dimensions: Accurate dimensions are provided for key elements, such as the height of the building, the width of windows and doors, and the spacing between features. These dimensions ensure that the building is constructed according to the design specifications. Crucially, elevation plans are created to scale, and have a specified scale marked on the plan, such as "1/4" = 1'0" or 1:50 (metric). This means that measurements can be taken directly from the plan using an architectural scale ruler.
Vertical Relationships: The plan illustrates the vertical relationships between different elements, such as the height of windows in relation to the floor level or the slope of the roof. This ensures that the building's proportions are aesthetically pleasing and that the design is structurally sound.
Ground Level: The elevation plan typically includes a reference to the ground level, indicating where the building meets the earth. This is important for understanding the building's relationship to its surroundings and for determining the correct placement of landscaping elements.
Overhangs and Projections: Features such as roof overhangs, balconies, and awnings are clearly indicated, showing how they project from the building's facade. This is important for understanding the building's overall shape and for ensuring that these features are properly supported.
Decorative Elements: Cornices, moldings, railings, and other decorative elements are meticulously drawn to convey the building's style and character. These details contribute significantly to the building's visual appeal and should be accurately represented in the elevation plan.
Adjacent Structures and Landscapes: Depending on the purpose and scope of the plan, it might also indicate the location of adjacent structures, landscaping features, and utilities. These elements can provide context and help to visualize the building within its environment.
In some instances, more detailed front elevation plans may also include surface textures and shadows to provide a more realistic representation of the building's appearance. This is particularly useful for communicating the building's aesthetic qualities to clients or stakeholders who may not be familiar with architectural drawings.
The Importance of Front Elevation Plans in the Design and Construction Process
Front elevation plans play a vital role in the entire building process, from initial design to final construction. Here are some of the key ways in which they contribute:
Design Visualization: The front elevation plan provides a visual representation of the building's exterior, allowing architects and clients to evaluate the design's aesthetic appeal and make necessary adjustments. It allows them to see how the building will look from the street and to assess its compatibility with the surrounding environment.
Communication Tool: The plan serves as a common language for communicating design ideas among architects, engineers, contractors, and clients. It ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding the building's appearance and features.
Permitting and Approval: Local authorities often require front elevation plans as part of the building permit application process. These plans are used to assess the building's compliance with zoning regulations, building codes, and design guidelines.
Construction Guidance: The plan provides detailed instructions for contractors and builders, specifying the dimensions, materials, and placement of various elements. It serves as a blueprint for the construction of the building's facade, ensuring accuracy and quality.
Cost Estimation: The plan helps in estimating the cost of materials and labor required for the building's exterior. By providing a detailed representation of the facade, it allows contractors to accurately calculate the quantities of materials needed and the time required for construction.
Landscaping and Site Planning: The front elevation plan provides valuable information for landscape architects and site planners. It helps them to understand the building's relationship to its surroundings and to design landscaping that complements the building's design.
Marketing and Sales: High-quality front elevation renderings can be used for marketing and sales purposes, helping to attract potential buyers or tenants. A well-designed elevation can showcase the building's aesthetic qualities and create a positive impression.
Historical Documentation: In some cases, front elevation plans are used for historical documentation purposes. They provide a record of the building's appearance at a particular point in time, which can be valuable for preservation and restoration efforts.
Common Types of Front Elevation Drawings
While the basic concept of a front elevation plan remains consistent, there are variations in the level of detail and representation techniques used, depending on the project's requirements and the stage of the design process. Some common types include:
Conceptual Elevations: These are preliminary drawings that are used to explore different design options and to communicate initial ideas. They may be less detailed than final elevations, focusing on the overall form and massing of the building.
Schematic Elevations: These drawings provide a more refined representation of the building's design, showing the placement of windows, doors, and other key features. They are typically used for design development and cost estimation.
Construction Documents: These are the most detailed and accurate elevations, used for construction purposes. They include precise dimensions, material specifications, and construction notes. These are also called working drawings or technical drawings.
Rendered Elevations: These are realistic representations of the building's appearance, created using computer software or traditional rendering techniques. They include details such as shading, textures, and landscaping, providing a more visually appealing presentation.
3D Elevations: These are three-dimensional models of the building's facade, which can be viewed from different angles. They provide a more comprehensive understanding of the building's form and spatial relationships. These may be exported as images for use as rendered elevations.
Interior Elevations: While the focus of this article is on front elevations, it's worth noting that interior elevations are also used to depict the vertical surfaces of interior spaces. These plans show the placement of fixtures, finishes, and other interior elements.
The choice of elevation type depends on the specific needs of the project and the intended audience. For example, a conceptual elevation might be sufficient for initial design discussions, while a construction document elevation is essential for building the project.
In conclusion, the front elevation plan is an indispensable tool in architecture and construction. Its ability to clearly and accurately represent a building's facade ensures effective communication, streamlines the construction process, and ultimately delivers the intended design vision.

What Is Front Elevation

A Floor Plan B Front Elevation C Side Scientific Diagram

Front Elevation Bungalow House Plans Plan

Help With A House Plan Front Elevation Pro Sketchup Community

Scheme Of The Tested Single Family House A Front Elevation B Scientific Diagram

Redesigning The Front Of A House To Improve Curb Appeal

Architecture House Plan And Elevation Complete Drawing Cadbullb Bungalow Floor Plans Building Designs

Front Elevation Designs Why Design Is Important

Floor Plan And Front Elevation Of The Case Study House Scientific Diagram

Residential Building Front Elevation Design 1824 Square Feet Designing