2 Bedroom House Building Plans: A Comprehensive Guide
The decision to build a house is a significant undertaking, often representing a substantial financial and emotional investment. For many individuals and small families, a two-bedroom house provides an optimal balance between affordability, space utilization, and future considerations. This article will explore the key aspects of two-bedroom house building plans, including design considerations, cost estimations, legal requirements, and the overall construction process.
Before diving into specific plans, it is crucial to define the project scope. This involves determining the budget, desired architectural style, land size, and anticipated lifestyle needs. A clear understanding of these foundational elements will streamline the planning and construction phases, minimize potential setbacks, and ensure the final product aligns with the homeowner's vision.
Understanding Design Considerations for 2 Bedroom Houses
Designing a two-bedroom house requires careful consideration of space optimization. Every square foot should be strategically allocated to maximize functionality and comfort. Several key design aspects warrant particular attention:
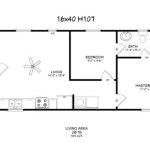
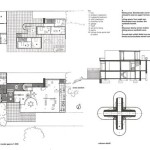
First, the floor plan is the cornerstone of any house design. For a two-bedroom house, popular floor plan options include ranch-style, bungalow, and two-story layouts. Ranch-style homes offer single-level living, making them ideal for individuals with mobility considerations. Bungalows often feature compact designs with efficient use of space, while two-story houses maximize land usage by stacking living spaces vertically.
Within the floor plan, the arrangement of rooms is paramount. The master bedroom should ideally be positioned away from high-traffic areas to ensure privacy and tranquility. The second bedroom can serve as a guest room, home office, or children's room. The living area, kitchen, and dining area should be seamlessly integrated to create a cohesive and inviting living space. Open-concept designs are frequently employed to enhance the feeling of spaciousness, particularly in smaller two-bedroom houses.
Bathroom design is another critical aspect. A single bathroom is sufficient for some two-bedroom houses, while others may benefit from an additional half-bath or ensuite bathroom attached to the master bedroom. The bathroom layout should prioritize functionality and accessibility, with ample storage and appropriate fixture placement.
Furthermore, integrating outdoor living spaces can significantly enhance the appeal of a two-bedroom house. A patio, deck, or porch provides an extension of the living area and offers opportunities for relaxation and entertainment. The design of these outdoor spaces should complement the architectural style of the house and consider the climate and surrounding environment.
Finally, Universal Design principles should be considered to ensure the long-term accessibility and adaptability of the house. Wider doorways, grab bars in bathrooms, and step-free entryways can make the house more comfortable and accessible for individuals of all ages and abilities. Incorporating these features during the planning stage can prevent costly renovations in the future.
Cost Estimation and Budgeting
Accurate cost estimation is essential for any construction project. Building a two-bedroom house involves numerous expenses, including land acquisition, architectural design fees, building permits, materials, labor, and landscaping. A comprehensive budget should account for all these costs, with a contingency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
The cost of land varies significantly depending on location, size, and zoning regulations. Obtaining a realistic estimate for land acquisition is the first step in the budgeting process. Architectural design fees typically range from 5% to 15% of the total construction cost, depending on the complexity of the design and the architect's experience.
Building permits are required for most construction projects and can vary in cost depending on the local municipality. Obtaining the necessary permits early in the process is crucial to avoid delays and potential fines. Materials represent a significant portion of the overall cost, including lumber, concrete, roofing, windows, doors, plumbing fixtures, electrical wiring, and appliances. Selecting cost-effective materials without compromising quality is essential for staying within budget.
Labor costs encompass wages for construction workers, including carpenters, plumbers, electricians, and painters. Labor rates vary depending on location and the skill level of the workers. Obtaining multiple quotes from different contractors is advisable to secure competitive pricing. Landscaping costs include grading, sodding, planting, and hardscaping. The extent of landscaping can significantly impact the overall cost of the project.
Furthermore, homeowners should factor in additional costs such as insurance, property taxes, and utility hookups. A detailed spreadsheet outlining all anticipated expenses will provide a clear picture of the total project cost and help identify areas where savings can be achieved. Regularly reviewing and updating the budget throughout the construction process is essential for maintaining financial control.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Navigating the legal requirements and regulations associated with building a house can be complex. Compliance with local zoning ordinances, building codes, and environmental regulations is crucial to avoid legal issues and ensure the safety and integrity of the structure.
Zoning ordinances regulate land use and dictate permissible building types, setbacks, height restrictions, and parking requirements. Before commencing any construction, homeowners must verify that their building plans comply with all applicable zoning regulations. Building codes establish minimum standards for construction practices, materials, and safety features. These codes cover aspects such as structural integrity, fire safety, plumbing, electrical systems, and energy efficiency.
Obtaining the necessary building permits is a critical step in the process. Permit applications typically require detailed construction plans, site plans, and engineering calculations. The permit review process ensures that the proposed construction meets all applicable codes and regulations. Inspections are conducted at various stages of construction to verify compliance with the approved plans and codes.
Environmental regulations may also apply, particularly in areas with sensitive ecosystems or protected species. Environmental impact assessments may be required to evaluate the potential effects of construction on the environment. Compliance with stormwater management regulations is essential to prevent erosion and pollution of waterways.
Moreover, homeowners should be aware of any homeowner association (HOA) rules and regulations that may apply. HOAs often have specific requirements regarding architectural design, landscaping, and property maintenance. Obtaining approval from the HOA before commencing construction is necessary to avoid potential conflicts.
Engaging with local authorities and consulting with legal professionals can help homeowners navigate the complex legal landscape and ensure compliance with all applicable regulations. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in costly fines, delays, or even the demolition of unauthorized structures.
The construction process itself involves several distinct stages, each requiring careful planning and execution. The initial stage involves site preparation, including clearing the land, grading the soil, and installing utilities. The foundation is then poured, providing a stable base for the structure.
Framing involves constructing the skeletal structure of the house, including walls, floors, and roof. Once the framing is complete, the exterior is enclosed with sheathing, roofing, and windows. Interior finishes include insulation, drywall, flooring, painting, and trim. Plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems are installed throughout the construction process.
Throughout the construction process, it is essential to maintain clear communication with the contractor and regularly inspect the work to ensure it meets quality standards. Change orders, which are modifications to the original plans, should be documented and approved in writing to avoid disputes. Upon completion of construction, a final inspection is conducted to verify compliance with all codes and regulations.
In summary, building a two-bedroom house requires careful planning, budgeting, and adherence to legal requirements. By understanding the design considerations, cost estimations, and regulatory framework, homeowners can navigate the construction process with confidence and create a comfortable and functional living space tailored to their needs.

2 Bedroom House Plan Lc70c Building Plans Small Modern Blueprints

12 Simple 2 Bedroom House Plans With Garages Houseplans Blog Com

Two Bedroom Small House Plan Cool Concepts Design Plans

2 Bedroom House Plans For Stylish Homes Ck

2 Bedroom House Plan Examples

2 Bedroom House Plan Examples

The Best 2 Bedroom Tiny House Plans Houseplans Blog Com

Practical 2 Bedroom House Plan With L Shaped Kitchen

2 Bedroom House Plans For Stylish Homes Ck

Modern 2 Bedroom House Plan 61custom Contemporary Plans