Understanding Spanish Floor Plans: A Guide to Design and Layout
Spanish floor plans, rooted in centuries of architectural evolution and cultural adaptation, offer a unique aesthetic and practical approach to residential design. These plans, often associated with Mediterranean architecture, are characterized by specific features that optimize living space, enhance natural light, and promote a connection with the outdoors. Understanding the core elements of Spanish floor plans provides valuable insight for homeowners, architects, and designers seeking to incorporate this distinctive style into their projects.
The historical context of Spanish architecture significantly influences the design principles found in these floor plans. Originating in Spain and spreading through its colonial territories, the style reflects a blend of Roman, Moorish, and indigenous influences. The arid climate of many regions where this style thrives necessitated design elements that promote coolness, ventilation, and protection from intense sunlight. Consequently, thick walls, courtyards, and strategic window placement are common features in Spanish floor plans.
Modern interpretations of Spanish floor plans often retain these traditional elements while incorporating contemporary amenities and technologies. The result is a harmonious blend of old-world charm and modern functionality. This article will explore the key aspects of Spanish floor plans, focusing on common layouts, distinctive architectural features, and the impact of regional variations.
Key Point 1: Common Layouts and Spatial Organization
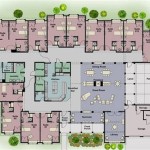
Spanish floor plans often exhibit a clear distinction between public and private spaces. The layout typically centers around a courtyard, which acts as a focal point and connects various areas of the house. This central courtyard, or patio, is not merely a decorative element; it serves as an outdoor living space, providing natural light and ventilation to the surrounding rooms.
The living areas, such as the living room (sala) and dining room (comedor), are typically located near the main entrance. These spaces are designed for entertaining guests and are often characterized by open layouts that promote social interaction. The kitchen (cocina) is usually situated adjacent to the dining room, facilitating ease of service during meals. Historically, the kitchen was often separated from the main living areas to contain cooking odors and heat, but modern designs often integrate the kitchen into the open floor plan.
Bedrooms (dormitorios) are typically grouped together in a separate wing of the house, providing a private and quiet retreat. Bathrooms (baños) are strategically located near the bedrooms, ensuring convenience and accessibility. Master suites often include a private bathroom and walk-in closet.
Service areas, such as the laundry room and storage spaces, are typically located in the back of the house, away from the main living areas. This separation helps to maintain the aesthetic appeal of the living spaces while providing functional utility.
Variations in layout can occur depending on the size and shape of the property. Smaller homes may feature a more compact layout with a smaller courtyard, while larger estates may incorporate multiple courtyards and expansive wings to accommodate various functions. However, the fundamental principle of separating public and private spaces remains a consistent feature in most Spanish floor plans.
The organization of space also extends to the vertical dimension. Two-story Spanish homes often feature a similar layout on both floors, with the upper floor typically dedicated to bedrooms and bathrooms. Balconies and terraces are common features on the upper floor, providing outdoor spaces with views of the surrounding landscape. Staircases are often designed as prominent architectural elements, adding visual interest to the interior.
Key Point 2: Distinctive Architectural Features
Several distinctive architectural features characterize Spanish floor plans, contributing to their unique aesthetic appeal and functional benefits. These features are often influenced by the climate and available materials in the regions where the style originated.
Thick walls, typically made of adobe or stucco, are a hallmark of Spanish architecture. These walls provide excellent insulation, helping to keep the interior cool during hot weather and warm during cold weather. The thickness of the walls also contributes to the soundproofing of the house, creating a quiet and peaceful living environment.
Arched doorways and windows are another common feature. Arches provide structural support while adding a touch of elegance and sophistication to the design. The curved lines of the arches soften the overall appearance of the house, creating a more inviting and welcoming atmosphere.
Tile roofs, typically made of terracotta or clay, are a defining characteristic of Spanish architecture. These roofs are not only visually appealing but also provide excellent protection from the elements. The curved shape of the tiles allows for efficient water runoff, preventing leaks and damage to the roof structure.
Courtyards are an integral part of Spanish floor plans, serving as outdoor living spaces and providing natural light and ventilation to the surrounding rooms. Courtyards are often landscaped with plants, trees, and fountains, creating a tranquil and relaxing environment. The courtyard also acts as a buffer between the interior of the house and the external environment, reducing noise and dust.
Wooden beams, often exposed, are another common feature. These beams add visual interest to the ceilings and provide structural support. The wood is typically stained or finished to enhance its natural beauty, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere. In some cases, the beams may be purely decorative, adding a rustic touch to the design.
Wrought iron details, such as window grilles, balconies, and gates, are often incorporated into Spanish architecture. These details add a touch of elegance and sophistication while providing security and protection. The intricate designs of the wrought iron work add visual interest to the exterior of the house.
Key Point 3: Regional Variations and Adaptations
While the fundamental principles of Spanish floor plans remain consistent, regional variations and adaptations reflect the diverse climate, culture, and available materials in different areas. These variations can be observed in the architectural details, materials used, and the overall layout of the house.
In California, Spanish Colonial Revival architecture is a popular style. This style often features white stucco walls, red tile roofs, and arched doorways. The interiors are typically characterized by hardwood floors, exposed wooden beams, and wrought iron details. The influence of the California climate is evident in the large windows and outdoor living spaces, designed to take advantage of the sunshine and mild temperatures.
In the Southwest, Spanish floor plans often incorporate elements of Native American architecture. Adobe walls, made of sun-dried earth, are a common feature. These walls provide excellent insulation, keeping the interior cool during the hot desert summers. The layout of the house may also be influenced by Native American traditions, with rooms arranged around a central courtyard.
In Florida, Spanish Mediterranean architecture is a popular style. This style often features stucco walls, tile roofs, and arched doorways, similar to Spanish Colonial Revival architecture. However, the Florida style may also incorporate elements of tropical design, such as lush landscaping and outdoor living spaces designed to take advantage of the warm, humid climate.
In Spain itself, regional variations reflect the diverse landscape and cultural traditions of different provinces. In Andalusia, the southern region of Spain, houses often feature whitewashed walls, tiled patios, and wrought iron details. In Catalonia, the northeastern region of Spain, houses may incorporate elements of Catalan Modernism, such as curved lines, decorative tiles, and stained glass windows.
Modern adaptations of Spanish floor plans often incorporate contemporary materials and technologies while retaining the fundamental principles of the style. For example, energy-efficient windows and insulation can be used to improve the thermal performance of the house. Solar panels can be installed on the roof to generate renewable energy. The layout of the house can be adapted to accommodate modern lifestyles, with open floor plans and flexible living spaces.
The enduring appeal of Spanish floor plans lies in their ability to combine beauty, functionality, and cultural significance. By understanding the key elements of these plans and the regional variations that exist, homeowners, architects, and designers can create spaces that are both aesthetically pleasing and practically suited to their needs.

Small Spanish Contemporary Plan
5 Bedroom Spanish Style House Plan With 4334 Sq Ft 134 1339

Two Story Spanish House Plan 9724

Spanish House Plan 1 Story Coastal Style Home Floor Mediterranean Plans New

Spanish Two Story House Plan 5493

Spanish Colonial 8303 4 Bedrooms And 3 5 Baths The House Designers

Two Story Spanish Style House Plan With Exercise Nook In Master Bath 36596tx Architectural Designs Plans

Spanish House Plan 175 1118 4 Bedrm 4948 Sq Ft Home Theplancollection

Small Spanish Contemporary House Plan 61custom Modern Plans Style Homes

Spanish House Plans Hacienda And Villa Style