Tiny House Design Plans: A Comprehensive Guide
Tiny house living has surged in popularity, driven by a desire for financial freedom, minimalist lifestyles, and environmental consciousness. A crucial aspect of this lifestyle shift is the thoughtful design of the tiny house itself. This article explores the key considerations and components of tiny house design plans.
The initial phase of planning involves defining the needs and lifestyle of the future occupants. This includes determining the number of residents, their daily activities, necessary appliances, and storage requirements. A thorough needs assessment forms the foundation for a functional and comfortable tiny home.
Budget constraints play a significant role in design choices. Establishing a realistic budget early in the planning process helps guide material selection, appliance choices, and overall design complexity. Accurate cost estimation prevents unexpected expenses and ensures the project remains within financial limits.
Choosing the right size is critical. While the typical tiny house ranges from 100 to 400 square feet, the optimal size depends on individual needs and local regulations. Larger spaces offer more comfort but increase construction costs and transportation complexity. Smaller spaces maximize affordability and mobility but demand clever space-saving solutions.
There are various tiny house styles to consider, each with unique aesthetic and functional characteristics. These include traditional craftsman styles, modern minimalist designs, rustic cabins, and contemporary industrial aesthetics. Selecting a style that aligns with personal preferences enhances the overall living experience.
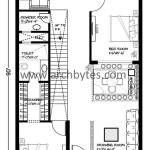
The layout is critical for maximizing space utilization and flow. Common layouts include lofted bedrooms for maximizing floor space, open floor plans for a sense of spaciousness, and multi-functional areas that serve various purposes throughout the day. Careful consideration of traffic flow and furniture placement is essential for creating a comfortable and efficient living environment.
Material selection significantly impacts both the aesthetic and structural integrity of the tiny house. Common building materials include wood framing, metal siding, and composite materials. Factors influencing material selection include cost, durability, maintenance requirements, and insulation properties. Sustainable and eco-friendly material options are also gaining popularity.
Incorporating essential features and amenities is essential for comfortable living. These may include a functional kitchen with efficient appliances, a well-designed bathroom with a composting toilet or small shower, and ample storage solutions integrated throughout the house. Prioritizing essential amenities ensures a functional and livable space.
Utilities and systems require careful planning. This includes designing efficient electrical systems, plumbing for water supply and drainage, and heating and cooling systems appropriate for the climate. Renewable energy solutions such as solar panels can be integrated for off-grid living, reducing environmental impact and long-term costs.
Compliance with local building codes and regulations is paramount. Regulations vary significantly by location, and obtaining necessary permits and inspections is crucial for legal occupancy and safety. Researching local regulations and working with experienced builders ensures compliance and avoids potential legal issues.
Professional design software can aid in visualizing the tiny house and creating detailed plans. Software programs allow for 3D modeling, virtual tours, and precise measurements, aiding in design refinement and communication with builders. These tools facilitate accurate material estimations and cost projections.
Collaborating with experienced builders or architects specialized in tiny house construction can streamline the process. Professionals provide valuable expertise in design, material selection, construction techniques, and navigating local regulations. Their experience can help avoid costly mistakes and ensure a high-quality build.
Pre-fabricated tiny houses or kits offer a convenient alternative to custom builds. Pre-fabricated options provide a faster construction timeline and often come with pre-installed utilities and appliances. These options offer a balance between customization and convenience, catering to various budgets and timelines.
Exploring existing tiny house plans online and in publications provides inspiration and practical guidance. Analyzing existing designs can spark new ideas and help visualize different layout options and design elements. This research phase allows for informed decision-making during the design process.
Considering transportation and mobility is crucial, particularly for those intending to relocate their tiny house frequently. Factors such as weight, dimensions, and towing requirements influence design choices. Designing for easy transportation simplifies relocation and expands lifestyle options.
Long-term maintenance and upkeep should be factored into the design. Choosing durable, low-maintenance materials and incorporating accessible systems simplifies ongoing maintenance tasks. Planning for maintenance minimizes future costs and extends the lifespan of the tiny house.

Tiny House Floor Plans With Lower Level Beds Tinyhousedesign Design

Tiny House Plan Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SL-731_FCP-83e310d6c4f4422a88bd36464339bf30.jpg?strip=all)
26 Tiny House Plans That Prove Bigger Isn T Always Better

10 X 20 Tiny Home Designs Floorplans Costs And Inspiration The Life

Tiny Home Plans House Floor And Designs

Tiny House Floor Plans 32 Home On Wheels Design

Studio500 Modern Tiny House Plan 61custom

Tiny House Plans For Houseplans Blog Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ana-tiny-house-58f8eb933df78ca1597b7980.jpg?strip=all)
4 Free Diy Plans For Building A Tiny House

Family Tiny House Design Floor Plans Layout