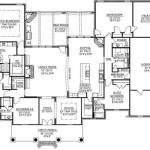
Tiny House on Wheels Plans
Tiny houses on wheels offer a unique blend of affordability, mobility, and minimal living. Building a tiny house, however, requires careful planning and consideration of specific design elements and legal requirements. Understanding available plans and resources is the first step in embarking on this journey.
Key Considerations Before Choosing a Plan
Several factors influence the optimal tiny house design. These factors impact the livability, functionality, and legal compliance of the finished structure. Careful consideration of these aspects ensures a successful build.
- Lifestyle and needs: How will the space be used daily? What are the essential amenities?
- Budget: Material costs, labor, and permit fees significantly influence design choices.
- Local regulations: Zoning and building codes vary by location, affecting size, height, and utility connections.
- Climate: Insulation, heating, and cooling systems require adjustment depending on the region's typical weather.
- Towing capacity: The weight and dimensions of the finished house must be compatible with the towing vehicle.
Types of Tiny House Plans
Various pre-designed plans cater to diverse preferences and needs. They provide detailed blueprints, material lists, and construction instructions, simplifying the building process. These plans cater to varying experience levels, from novice DIYers to experienced builders.
- DIY Plans: Designed for individuals comfortable with construction, offering flexibility and cost savings.
- Pre-drawn Plans: Professionally drafted blueprints available for purchase, ensuring accurate measurements and structural integrity.
- Custom Plans: Tailored designs created by architects or designers, addressing specific requirements and preferences.
Essential Components of a Tiny House Plan
A comprehensive tiny house plan outlines the essential components of the structure. These details ensure the safety, functionality, and longevity of the dwelling.
- Floor plans: Illustrate the layout of rooms and the placement of fixtures.
- Elevations: Show the exterior views of the house from different angles.
- Sections: Provide cross-sectional views of the house, revealing wall construction and framing details.
- Foundation and framing plans: Detail the structural support system of the tiny house.
- Electrical and plumbing diagrams: Outline the location of wiring, outlets, pipes, and fixtures.
- Roof plan: Specifies the roof design, materials, and drainage system.
Finding Reputable Tiny House Plan Providers
Numerous online and offline resources offer tiny house plans. Choosing a reputable provider is crucial for obtaining accurate, complete, and reliable plans. Evaluating providers based on their experience and the quality of their offerings is essential.
- Architects specializing in tiny houses: Offer customized designs tailored to specific needs and preferences.
- Online marketplaces for tiny house plans: Provide a wide selection of pre-drawn plans from various designers.
- Tiny house builders: May offer their own in-house plans for clients to purchase.
- Reputable tiny house communities and blogs: Often recommend trusted plan providers based on community feedback.
Understanding Plan Specifications and Terminology
Familiarizing oneself with common architectural terms and specifications is essential for interpreting and utilizing tiny house plans effectively. Understanding these elements ensures a smooth construction process.
- R-value: Measures the thermal resistance of insulation.
- Load-bearing walls: Support the weight of the roof and upper floors.
- Sheathing: Protective covering applied to the exterior walls.
- Fenestration: Refers to the arrangement of windows and doors.
Modifying Existing Tiny House Plans
While pre-drawn plans offer a convenient starting point, modifications are often necessary to suit individual needs. It is important to consult with structural engineers when making significant changes to ensure the integrity of the design.
- Adjusting room sizes and layouts to accommodate specific furniture or appliances.
- Adding or removing windows and doors to optimize natural light and ventilation.
- Modifying rooflines or adding lofts to maximize headroom and storage space.
Legal Considerations and Permitting
Building a tiny house on wheels typically requires adherence to specific regulations. Consulting local authorities to understand and comply with building codes and zoning laws is critical to avoid legal issues.
- Building permits: Ensure compliance with local building codes and safety standards.
- Zoning regulations: Determine where tiny houses on wheels are permitted.
- Trailer registration and insurance: Required for legal transportation on public roads.
Building Your Tiny House: Resources and Support
The process of building a tiny house can be challenging. Utilizing available resources and seeking support from experienced builders or online communities can significantly aid the construction process.
- Tiny house workshops and building classes: Provide hands-on training and guidance.
- Online forums and communities: Offer advice, support, and resources from experienced tiny house dwellers.
- Contractors specializing in tiny house construction: Can assist with specific aspects of the build or manage the entire project.

Tiny House Floor Plans 32 Home On Wheels Design

Design A Tiny House On Wheels Tips And Tools For Diyers

Escape Traveler A Tiny House On Wheels That Comfortably Sleeps 6 Floor Plans

Free Tumbleweed Diy Tiny House Plans Houses

Tiny House Plans The Project

27 Adorable Free Tiny House Floor Plans Craft Mart

How To Pick The Best Tiny House On Wheels Floor Plan Wayward Home

224 Sq Ft Tiny House On Wheels By Living Homes Diy Small

The Top Tiny House Plans For A Diy In 2024

Floor Plans For Your Tiny House On Wheels Photos