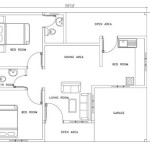
Beach Homes on Stilts: Plans and Considerations
Beach homes on stilts, also known as pile dwellings or elevated homes, represent a unique and often necessary housing solution in coastal regions. These structures are built on pillars or stilts, raising the main living area above ground level. This design offers numerous advantages, including protection from flooding, storm surges, erosion, and pests. However, the planning and construction of beach homes on stilts require careful consideration of various factors, including local building codes, environmental regulations, and the specific characteristics of the building site.
The architectural plans for a beach home on stilts are significantly different from those of a traditional ground-level home. They must account for the structural integrity of the stilts, the load-bearing capacity of the soil, and the overall stability of the building. Moreover, accessibility considerations, such as stairs or elevators, must be incorporated into the design. This article explores the key aspects of planning beach homes on stilts, examining the different types of stilt foundations, the relevant design considerations, and the regulatory requirements involved.
Understanding Stilt Foundation Types
The foundation is arguably the most critical component of a beach home on stilts. The choice of foundation type depends on several factors, including the soil conditions, the local climate, the height of the pilings, and the overall design of the house. Incorrect foundation selection can lead to structural instability, increased maintenance costs, and even potential failure of the building.
Concrete Pilings: Concrete pilings are a popular choice for stilt foundations due to their durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. They are typically driven deep into the ground to provide a solid and stable support for the structure. Concrete pilings can be pre-cast or poured in place, depending on the site conditions and the availability of resources. One of the main advantages of concrete pilings is their ability to withstand the harsh conditions of a marine environment, including saltwater exposure and wave action. Furthermore, they are relatively low-maintenance and have a long lifespan.
Wood Pilings: Wood pilings, traditionally crafted from treated timber, offer a more cost-effective alternative to concrete pilings. However, their use is often limited to areas where the risk of flooding and storm surge is lower. The type of wood and the treatment process are crucial factors in determining the longevity of wood pilings. Pressure-treated wood is commonly used to protect against rot, insects, and marine borers. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to prevent deterioration and ensure the structural integrity of wood pilings. In some regions, specific types of wood known for their natural resistance to decay, such as cypress or cedar, may be preferred.
Steel Pilings: Steel pilings offer a high strength-to-weight ratio and can be driven to considerable depths, making them suitable for areas with unstable soil conditions. They are also resistant to corrosion, especially when coated with protective materials. Steel pilings can be used in conjunction with concrete or wood to create a hybrid foundation system. However, steel pilings can be more expensive than other options, and their installation may require specialized equipment. Regular inspections are necessary to identify and address any signs of corrosion or damage.
Helical Piles: Helical piles, also known as screw piles, are a modern foundation solution that offers several advantages over traditional piling methods. They consist of steel shafts with helical bearing plates that are screwed into the ground. Helical piles can be installed quickly and efficiently, with minimal disturbance to the surrounding soil. They are also suitable for a wide range of soil conditions and can be used in both residential and commercial applications. Helical piles are particularly useful in areas where access is limited or where traditional piling methods are not feasible.
Design Considerations for Elevated Beach Homes
Designing a beach home on stilts requires careful attention to several key considerations, including structural integrity, accessibility, ventilation, and aesthetics. The goal is to create a safe, functional, and visually appealing home that can withstand the challenges of a coastal environment.
Structural Integrity: The primary concern in designing a beach home on stilts is ensuring its structural integrity. The stilts must be able to support the weight of the house, as well as withstand the forces of wind, waves, and seismic activity. This requires a thorough understanding of the local climate, soil conditions, and building codes. Structural engineers play a crucial role in designing the foundation and framing system to ensure that the house is stable and secure. The plans must specify the size, spacing, and material of the stilts, as well as the connections between the stilts and the house.
Accessibility: Accessibility is another important consideration in the design of beach homes on stilts. Since the main living area is elevated above ground level, access must be provided via stairs, ramps, or elevators. The choice of access method depends on the height of the stilts, the needs of the occupants, and the available space. Stairs are the most common and cost-effective option, but they may not be suitable for individuals with mobility issues. Ramps provide a more gradual slope and are accessible to wheelchairs and other mobility devices. Elevators offer the most convenient and accessible solution but are also the most expensive and require regular maintenance.
Ventilation: Proper ventilation is essential for preventing moisture buildup and maintaining a comfortable indoor environment in beach homes on stilts. The space beneath the house should be well-ventilated to allow air to circulate and prevent the accumulation of moisture. This can be achieved by providing adequate openings in the foundation walls or by installing vents. The design should also consider the prevailing wind direction and ensure that the openings are positioned to maximize airflow. In addition to under-house ventilation, the house itself should be designed with adequate ventilation to reduce the risk of mold and mildew growth.
Aesthetics: While functionality and structural integrity are paramount, aesthetics also play a significant role in the design of beach homes on stilts. The house should be designed to blend in with the surrounding environment and to complement the natural beauty of the coastline. The choice of materials, colors, and architectural style can all contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of the house. Many homeowners opt for a coastal or beach-inspired design, featuring natural materials, light colors, and large windows to take advantage of the views. Landscaping can also be used to enhance the aesthetic appeal of the house and to create a relaxing and inviting outdoor space.
Flood-Resistant Design: Given the susceptibility of coastal areas to flooding, incorporating flood-resistant design elements is critical. This includes elevating the lowest floor above the base flood elevation (BFE), using flood-resistant materials for construction below the BFE, and ensuring proper drainage around the foundation. The design should also consider the potential for wave action and storm surge and incorporate measures to protect the house from damage. This may include using breakaway walls, anchoring the house to the foundation, and installing storm shutters.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements and Building Codes
Building a beach home on stilts requires compliance with a complex set of regulatory requirements and building codes. These regulations are designed to protect public safety, minimize environmental impact, and ensure the long-term durability of the structure. It is essential to consult with local authorities and experienced professionals to ensure that all requirements are met.
Local Building Codes: Local building codes typically address a wide range of issues related to the design and construction of beach homes on stilts, including foundation requirements, structural standards, accessibility guidelines, and energy efficiency standards. These codes may vary depending on the specific location and may be more stringent in areas that are prone to flooding or other natural hazards. It is crucial to obtain a copy of the local building codes and to review them carefully before starting the design process.
Environmental Regulations: Environmental regulations are designed to protect the natural resources of the coastal zone, including wetlands, dunes, and beaches. These regulations may restrict the location and size of beach homes on stilts, as well as the types of materials that can be used in construction. Some areas may require environmental impact assessments to be conducted before construction can begin. It is important to consult with environmental agencies and to obtain all necessary permits before starting any work.
Floodplain Management Regulations: Floodplain management regulations are designed to minimize the risk of flood damage to property and to protect the natural functions of floodplains. These regulations typically require that beach homes on stilts be elevated above the base flood elevation (BFE) and that they be designed to withstand the forces of floodwaters. The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) provides flood insurance to homeowners in participating communities and establishes minimum standards for floodplain management. Compliance with floodplain management regulations is essential for obtaining flood insurance and for protecting the value of the property.
Permitting Process: The permitting process for building a beach home on stilts can be complex and time-consuming. It typically involves submitting detailed plans and specifications to local authorities for review and approval. The plans must demonstrate compliance with all applicable building codes, environmental regulations, and floodplain management regulations. In some cases, public hearings may be required to allow community members to comment on the proposed project. It is advisable to work with an experienced architect or engineer who is familiar with the local permitting process to ensure that all requirements are met and that the project is approved in a timely manner.
Planning a beach home on stilts involves careful selection of foundation type, consideration of design factors, and a thorough understanding of regulatory requirements. Attention to these details ensures a durable, safe, and aesthetically pleasing home that integrates well with the coastal environment.

Beach House Plans Coastal Home Great Design

Beach House Floor Plans Coastal Carriage

House Design Plan Ch539 3 Stilt Plans On Stilts Carriage

Home Plan Ch464

Plan 44026td Classic Florida Er Beach House Plans Coastal

Home Plan Ch546

Beach House Plans Archives From Home Designs

Coastal House Plan Ch672

Family S 576 Sq Ft Stilt Beach House

Beach House Plans Archives From Home Designs