Essential Aspects of Cob House Design Plans
Cob houses, crafted from a mixture of clay, sand, straw, and other natural materials, offer a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to conventional construction. Designing a cob house requires careful consideration of specific aspects to ensure structural integrity, thermal comfort, and aesthetic appeal. Here are the essential elements that should be meticulously planned in a cob house design:
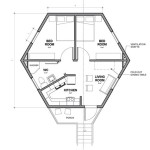
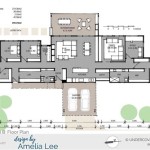
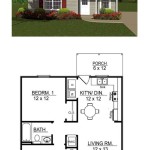
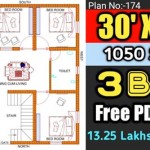
1. Site Selection and Foundation:
The foundation of a cob house heavily influences its stability and durability. The site should have adequate drainage to prevent water damage, and the foundation should be designed to withstand the weight of the cob walls. Proper site grading and the incorporation of a stone or concrete footing are essential for a sound foundation.
2. Wall Thickness and Openings:
Cob walls provide significant thermal mass, regulating indoor temperatures. The thickness of the walls should be carefully calculated based on the local climate and desired thermal performance. Windows and doors create openings in the cob walls and should be judiciously planned to balance natural light and ventilation without compromising structural integrity.
3. Roof Structure:
The roof of a cob house protects it from the elements and supports the weight of additional materials like thatch or tiles. The roof structure should be designed to handle the expected snow and wind loads in the area. Proper sealing and flashing around roof penetrations are crucial to prevent leaks and water damage.
4. Thermal Performance:
Cob houses are inherently energy-efficient due to their thermal mass. However, additional measures can be incorporated to enhance thermal performance. Insulating the roof, installing double-glazed windows, and optimizing solar orientation through passive design strategies can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs.
5. Ventilation and Moisture Management:
Proper ventilation is essential in cob houses to prevent moisture buildup and maintain indoor air quality. Natural ventilation through windows, vents, and passive airflow should be carefully planned to minimize humidity and ensure a healthy indoor environment.
6. Interior Finishes:
The interior finishes of a cob house contribute to its aesthetic appeal and comfort. Cob walls can be left exposed, showcasing their natural beauty, or they can be coated with plasters, lime washes, or clay paints. Natural materials like wood, stone, and wool can be incorporated into the interior design to create a cohesive and inviting atmosphere.
7. Green Building Practices:
Cob houses inherently align with green building principles. They utilize sustainable materials, minimize waste during construction, and promote energy efficiency. By incorporating additional features like rainwater harvesting, solar panels, and composting systems, the environmental impact of a cob house can be further reduced.
Designing a cob house is a collaborative process that involves careful planning, skilled craftsmanship, and an appreciation for sustainable building practices. By considering these essential aspects, architects, builders, and homeowners can create beautiful, durable, and environmentally friendly cob homes that stand the test of time.

Cob House Floor Plans For The Home

Image Detail For Cob House Plans Submited Images Pic 2 Fly Floor

Seismic Engineering Diagram Cob House Plans Eco Design

Cob House Plan Inspiration Kerpiç Ev Tasarım Evler

English Earthbag Cottage Plan Cob House Plans Round

Gallery An Off Grid Cob Retreat On A Private Bluff House Plans Floor

Security Check Required Castle House Plans Floor Plan

Stunning Mud And Wood Architecture

Tiny Cob House Plans The Freeman This

Best House For Hot Humid Climate Green Building Forum At Permies Cob Plans Tiny