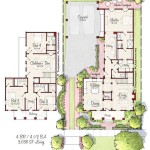
Drawing a Home Floor Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
Creating a home floor plan is a fundamental step in any construction, renovation, or interior design project. It serves as a visual representation of a building’s layout, demonstrating the spatial relationships between rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other architectural elements. A well-executed floor plan is crucial for effective communication between architects, builders, contractors, and homeowners, ensuring that the final result aligns with the intended design and functional requirements.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to the process of drawing a home floor plan, covering essential considerations, techniques, and tools that are fundamental in creating an accurate and informative representation. It delves into the importance of understanding scale, measuring techniques, representation conventions, and the various software options available for both manual and digital floor plan creation.
Before embarking on the drawing process, it is important to understand the specific project requirements. Are you planning a new build, a renovation, or simply redesigning the interior of an existing space? The scope of the project influences the level of detail required in the floor plan. A new build requires a comprehensive plan encompassing all structural elements, while a renovation might focus on specific areas of modification. Interior design projects emphasize the layout of furniture, fixtures, and equipment within the existing structure.
Gathering information is the next crucial step. This involves obtaining existing blueprints, reviewing property surveys, and conducting thorough site measurements. For existing buildings, accurate measurements are paramount. If blueprints are unavailable, meticulously measuring each room, wall, door, and window is necessary. Use a reliable measuring tool, such as a laser distance measurer, to ensure accurate and consistent data collection. Consistent and accurate measurements form the foundation of a reliable floor plan.
Once you have gathered the necessary data and determined the scope of your project, you can begin the process of drawing the floor plan. Whether you choose to use traditional drafting methods or digital software, a solid understanding of the basics is essential for creating a high-quality, usable document.
Understanding Scale and Representation
Scale is a fundamental concept in floor plan design. It represents the ratio between the dimensions on the drawing and the actual dimensions of the real-world space. Selecting an appropriate scale is crucial for ensuring that the floor plan is both manageable and detailed. A typical scale for residential floor plans is 1/4 inch = 1 foot (1:48), meaning that every quarter inch on the drawing represents one foot in reality. Smaller scales, such as 1/8 inch = 1 foot (1:96), may be used for larger buildings or when displaying an overview of the entire property.
Understanding different line weights and their significance is important for clear communication. Thicker lines are typically used to represent exterior walls and structural elements, while thinner lines designate interior walls, doors, and windows. Dashed lines can represent elements above or below the plane of the floor, such as soffits or foundations. Consistent use of standard architectural symbols for doors, windows, fixtures, and appliances is also essential for clarity and ease of interpretation. Refer to architectural drafting standards for a comprehensive list of symbols and conventions.
Representing wall thicknesses accurately is important for correctly estimating construction costs and ensuring adequate space for fixtures and appliances. Walls are typically drawn to scale, reflecting their actual thickness. For example, a 6-inch thick wall would be represented as 1/8 inch on a floor plan drawn at a scale of 1/4 inch = 1 foot. Accurately depicting wall thicknesses is critical, especially when planning for built-in cabinetry, plumbing, and electrical systems.
Door swings and window placement are also critical aspects of floor plan representation. Indicate the direction in which doors open and the size of the opening. This helps visualize circulation patterns and ensures that doors do not interfere with furniture placement or create awkward traffic flow. Windows should be accurately positioned and sized, indicating the type of window (e.g., casement, double-hung) and the direction of operation. Consider the impact of natural light and ventilation when determining window placement.
Annotation is crucial for conveying important information that cannot be represented graphically. Label each room with its intended use (e.g., bedroom, kitchen, living room). Dimension lines should clearly indicate the length and width of each room, as well as the overall dimensions of the building. Include notes to specify materials, finishes, and other relevant details, such as ceiling heights, flooring types, and the locations of electrical outlets and switches. Clear and concise annotations enhance the usability and clarity of the floor plan.
Manual Drafting Techniques
Traditional manual drafting involves using drafting tools such as pencils, T-squares, triangles, scales, and erasers to create floor plans on paper or vellum. While digital software has become increasingly prevalent, understanding manual drafting techniques can provide valuable insights into the principles of floor plan design. Manual drafting encourages precision, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of spatial relationships.
Start by establishing a reference point and grid lines on the drafting surface. These lines provide a framework for accurately positioning walls, doors, and other elements. Use a T-square to draw horizontal lines and a triangle to draw vertical lines, ensuring that all lines are perpendicular to each other. This creates a consistent and accurate grid system that helps maintain the correct scale and proportions.
Use a scale ruler to measure and mark the locations of walls, doors, and windows. Carefully transfer measurements from your site survey to the floor plan, ensuring that all dimensions are accurate and consistent with the chosen scale. Use different line weights to distinguish between exterior walls, interior walls, and other architectural elements. Apply architectural symbols using templates or freehand techniques, ensuring that they are consistent with industry standards.
Pay close attention to the details of each element, such as door swings, window types, and fixture placement. Double-check all measurements and annotations to ensure accuracy and completeness. Manual drafting requires patience and attention to detail, but it can result in a high-quality floor plan that accurately represents the design intent.
While manual drafting offers a hands-on approach to floor plan design, it can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Corrections can be challenging, requiring the use of erasers and the potential for smudging or damaging the drafting surface. Digital software offers several advantages over manual drafting, including increased efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility.
Utilizing Digital Floor Plan Software
Digital floor plan software has revolutionized the process of creating and modifying architectural drawings. These programs offer a wide range of tools and features that streamline the design process, improve accuracy, and facilitate collaboration. Digital floor plan software typically provides pre-drawn architectural elements, automated dimensioning, and 3D visualization capabilities, enabling users to create professional-quality floor plans with ease.
Several software options are available, ranging from free online tools to professional-grade CAD (Computer-Aided Design) programs. Free online tools often offer basic functionality and are suitable for simple floor plans or quick sketches. Professional-grade CAD programs, such as AutoCAD, Revit, and ArchiCAD, provide advanced features for creating complex architectural drawings, including BIM (Building Information Modeling) capabilities. BIM allows architects and engineers to create a digital representation of a building that includes not only its physical geometry but also its functional characteristics and performance data.
When selecting a floor plan software, consider your specific needs and budget. Evaluate the software's ease of use, feature set, compatibility with other software, and available support resources. Start with a free trial or demonstration version to familiarize yourself with the software's interface and capabilities. Many software programs offer tutorials and online documentation to help users learn the basics and master advanced techniques.
Creating a floor plan using digital software typically involves defining the walls, doors, and windows, placing fixtures and appliances, and adding annotations and dimensions. The user can select pre-drawn elements from the software's library or create custom elements using drawing tools. Accurate measurements are essential for creating a realistic and functional floor plan. Digital software often includes automated dimensioning tools that can automatically calculate and display the dimensions of rooms, walls, and other elements.
One of the key advantages of digital floor plan software is the ability to easily modify and iterate on the design. Changes can be made quickly and easily without having to redraw the entire floor plan. Digital software also facilitates collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and modify the same file simultaneously. This is particularly important for complex projects involving multiple stakeholders, such as architects, engineers, contractors, and homeowners.
Exporting the floor plan in various formats, such as PDF, DWG, or JPG, is crucial for sharing the design with others. PDF format is ideal for printing and viewing on different devices, while DWG format is commonly used for exchanging files with other CAD programs. High-resolution JPG images can be used for presentations and marketing materials.
Digital floor plan software significantly enhances the efficiency and accuracy of the design process, making it an indispensable tool for architects, designers, and homeowners. However, it is important to remember that the software is only a tool, and a solid understanding of architectural principles and drafting conventions is still essential for creating a high-quality floor plan.
Key Considerations for Accuracy and Functionality
Accuracy is paramount in floor plan creation, as even minor errors can have significant consequences during construction or renovation. Double-checking all measurements, dimensions, and annotations is crucial for ensuring that the floor plan is accurate and reliable. Use a reliable measuring tool and carefully transfer measurements from the site survey to the floor plan. Avoid making assumptions or approximations, and always verify your data. Errors in a floor plan can lead to costly mistakes and delays during the building process.
Compliance with building codes and regulations is another critical consideration. Ensure that the floor plan complies with all applicable building codes, zoning ordinances, and accessibility requirements. Consult with local building officials or a qualified architect to verify compliance. Building codes address various aspects of construction, including structural integrity, fire safety, ventilation, and energy efficiency. Failure to comply with building codes can result in fines, delays, and even the rejection of the building permit.
Functionality is a key aspect of floor plan design. The layout of the space should be functional, efficient, and conducive to the intended use. Consider the flow of traffic, the relationships between different rooms, and the placement of furniture and fixtures. A well-designed floor plan should minimize wasted space and maximize usability. Think about how the space will be used and how people will move through it. For example, the kitchen should be located near the dining area, and the bedrooms should be located away from noisy areas.
Accessibility is an increasingly important consideration in floor plan design. Ensure that the floor plan is accessible to people with disabilities, complying with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) guidelines or similar accessibility standards. This includes providing adequate clearances for wheelchairs, ramps, and accessible bathrooms. Consider the needs of all potential users when designing the floor plan, including those with mobility impairments, visual impairments, and hearing impairments.
Finally, sustainability should be integrated into the floor plan design. Consider the use of sustainable materials, energy-efficient appliances, and passive solar design strategies. Optimize the orientation of the building to maximize natural light and ventilation, reducing the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning. Implement water-saving fixtures and appliances to conserve water. By incorporating sustainable design principles, you can create a floor plan that is both environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
Creating a home floor plan is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a solid understanding of architectural principles. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can create a high-quality floor plan that accurately represents the design intent and facilitates successful construction or renovation projects.

Floor Plan Creator And Designer Free Easy App

Floor Plans Types Symbols Examples

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

Floor Plans Types Symbols Examples

House Plan Drawing Everything You Need To Know

Draw Floor Plans In Half The Time Cedreo

Home Floor Plans House Plan Drawings

Draw Floor Plans In Half The Time Cedreo

Easy Home Building Floor Plan Cad Pro

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan