Floor Plan Dimension Rules
Creating accurate and readable floor plans requires adherence to specific dimensioning rules. These rules ensure clarity and prevent misinterpretations that can lead to costly errors during construction. This article outlines key principles and practices for effectively dimensioning floor plans.
Overall Dimensioning Strategies
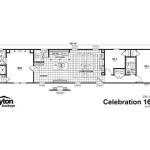
A well-dimensioned floor plan utilizes a combination of strategies to convey the complete size and layout of a space. Generally, a series of interconnected chains or loops of dimensions are used, rather than a redundant and cluttered approach. The placement of dimensions should be logical and easy to follow, enabling anyone reviewing the plan to understand the relationships between various building elements.
Dimensioning Exterior Walls
Exterior wall dimensions are crucial for establishing the overall footprint of the building. These dimensions should be placed outside the wall lines and indicate the overall length and width of each wall segment. Breakdowns of individual components, such as windows and doors, should be included within the overall wall dimension string.
Dimensioning Interior Walls
Interior wall dimensions define the sizes and locations of rooms and spaces within the building. These dimensions are typically placed inside the room or space being defined. Where space allows, dimensions can be placed between parallel walls to clearly represent the distance between them. For smaller spaces, dimensions may be placed outside the room with extension lines referencing the interior walls.
Dimensioning Doors and Windows
Accurate dimensions for doors and windows are essential for ordering and installation. These dimensions typically include the width of the opening and, in the case of windows, the height as well. The location of doors and windows within a wall segment should be clearly dimensioned from wall ends or other reference points.
Dimensioning Other Building Elements
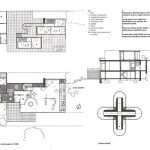
Other building elements, such as built-in fixtures, fireplaces, and structural columns, require clear dimensioning. These dimensions should indicate the size and location of the element within the overall floor plan. For complex elements, separate detail drawings may be necessary to provide complete dimensional information.
Units of Measurement
Consistency in units of measurement is paramount in floor plan dimensioning. The chosen unit, typically feet and inches or millimeters, should be clearly indicated on the plan. All dimensions throughout the plan must adhere to this chosen unit to avoid confusion and errors.
Dimension Placement and Readability
Dimensions should be placed in a clear and organized manner, avoiding overlapping lines or cluttered areas. Sufficient spacing between dimension lines and other plan elements enhances readability. Text should be oriented to be read from the bottom or right side of the drawing. Consistent font size and style contributes to a professional and easily understood plan.
Use of Extension and Dimension Lines
Extension lines, thin lines extending outwards from the object being dimensioned, should not touch the object itself, leaving a small gap for clarity. Dimension lines, capped with arrowheads or slashes, indicate the boundaries of the dimension and feature the numerical measurement. These lines should be positioned at consistent distances from the object being measured and arranged in a logical sequence to guide the reader's eye.
Dealing with Complex Shapes
For irregularly shaped rooms or building elements, dimension strategies need to adapt. Breaking down complex shapes into smaller, simpler geometric figures can simplify the dimensioning process. Radial dimensions can be used for curved walls or elements. Accurate dimensioning of angles is crucial in representing complex geometries.
Importance of Accuracy
Accuracy is paramount in floor plan dimensioning. Every dimension must be precise to ensure that the built structure matches the intended design. Double-checking measurements and using appropriate tools for dimensioning contribute significantly to the accuracy and reliability of the floor plan.
Coordination with Other Drawings
Floor plans need to coordinate seamlessly with other construction documents, such as elevations and sections. Dimensions should be consistent across all drawings to avoid conflicts and ensure a cohesive representation of the building design. This consistency is vital for accurate construction and avoids costly rework due to dimensional discrepancies.

Dimensioning Rules For Architectural Floor Plans By Joe Caruso On Prezi Next

Architectural Graphic Standards Life Of An Architect

How To Read A Floor Plan With Dimensions Houseplans Blog Com

12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

How To Properly Read Floor Plans And What Details Look For

How To Read A Floor Plan With Dimensions Houseplans Blog Com

Architectural Graphic Standards Life Of An Architect

Essential Measurements For Space Planning Your Home Houzz

Floor Plans With Dimensions Including Examples Cedreo

Floor Plans With Dimensions Including Examples Cedreo