How to Read House Plan Blueprints
Understanding house plan blueprints is crucial for anyone involved in the construction or renovation of a home. Blueprints provide a visual representation of the intended structure, detailing everything from the layout and dimensions to the materials and specifications. Learning to interpret these drawings effectively facilitates clear communication between architects, contractors, and homeowners, ultimately contributing to a successful project.
Blueprints typically consist of a series of drawings organized into sets. These sets often include floor plans, elevations, sections, foundation plans, and details. Each drawing type offers a unique perspective on the house design, and understanding their respective purposes is the first step in blueprint comprehension.
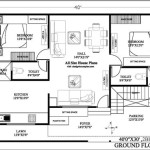
Floor plans offer a bird's-eye view of the house layout. They depict the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and fixtures as they would appear if the roof were removed. Floor plans are essential for visualizing the flow of space within the house and understanding the relationship between different areas.
Elevation drawings depict the exterior walls of the house from different viewpoints, such as the front, back, and sides. These drawings show the vertical dimensions of the house, including the height of walls, roofs, windows, and doors. Elevations provide crucial information about the exterior appearance and architectural style of the house.
Section drawings provide a cutaway view of the house, revealing its internal structure. These drawings are similar to slicing the house vertically and looking at the exposed surfaces. Sections show the relationship between different levels, the construction of walls, floors, and roofs, and the placement of structural elements.
Foundation plans illustrate the layout of the foundation walls, footings, and other structural elements that support the house. These drawings are critical for understanding the groundwork and ensuring the stability of the structure. They often include details about materials, dimensions, and reinforcement requirements.
Detail drawings provide close-up views of specific building components, such as windows, doors, stairs, and wall sections. These drawings offer intricate details about the construction and assembly of these elements, including materials, dimensions, and connections. Details are essential for contractors and builders to ensure accurate construction according to the architect's specifications.
Blueprints utilize a standardized set of symbols and annotations to convey information concisely. Lines of varying thickness and style represent different elements, such as walls, doors, windows, and utilities. Understanding these symbols is essential for interpreting the drawings accurately.
Dimensions are crucial components of blueprints, indicating the size and location of various elements. They are typically represented as numerical values accompanied by dimension lines and extension lines. Accurate interpretation of dimensions is critical for ensuring that the construction adheres to the intended design.
Scales are used to represent the actual size of the house on the smaller scale of the blueprint. Blueprints typically indicate the scale used, such as 1/4 inch equals 1 foot. Understanding the scale allows one to translate the dimensions on the blueprint to real-world measurements.
Annotations, notes, and specifications provide additional information about materials, construction methods, and other relevant details. These annotations supplement the graphical information on the blueprints and offer further clarification for builders and contractors.
Abbreviations are commonly used in blueprints to save space and simplify representation. Familiarizing oneself with common architectural abbreviations is helpful for understanding the annotations and specifications.
The title block, typically located on each drawing sheet, provides essential information about the project, including the project name, client name, architect's name, drawing title, drawing number, and revision date. Reviewing the title block ensures that one is working with the correct set of drawings and the most up-to-date version.
Understanding the different drawing types, symbols, dimensions, and annotations is essential for effectively reading house plan blueprints. Taking the time to study and interpret these elements can contribute to a smoother construction process and a more successful project outcome. Consulting with architects or experienced builders can provide further guidance and clarification when needed.
Utilizing online resources and software tools can also aid in the visualization and interpretation of blueprints. Many programs allow users to view blueprints in 3D, providing a more immersive and comprehensive understanding of the design.
Practicing blueprint reading with simpler examples, such as small sheds or garages, can build confidence and proficiency before tackling more complex house plans. Analyzing these simpler drawings allows one to become familiar with the basic principles and symbols before moving on to larger projects.
Keeping a notebook or digital document to record notes and observations while reviewing blueprints can be a valuable practice. This allows one to track questions, clarifications needed, and any potential discrepancies identified during the review process.

How To Read A Floor Plan With Dimensions Houseplans Blog Com

How To Properly Read Floor Plans And What Details Look For

How To Read House Plans The Construction Set

How To Read A Floor Plan With Dimensions Houseplans Blog Com

How To Read Blueprints

How To Read House Plans Floor Building In 10 Minutes Archid

How To Read A Floor Plan

How To Read A Floor Plan

How To Read Floor Plans

How To Read Blueprints And Floor Plans