Insulated Dog House Plan: Providing Year-Round Comfort for Your Canine Companion
Providing adequate shelter is a fundamental aspect of responsible dog ownership. A well-designed and insulated dog house offers protection from the elements, creating a comfortable and safe haven for a dog regardless of the season. An insulated dog house plan involves carefully selecting materials, incorporating insulation techniques, and considering factors such as size and ventilation to create an optimal environment for the dog's well-being. This article delves into the key considerations and practical steps involved in developing and implementing an effective insulated dog house plan.
Key Considerations in Designing an Insulated Dog House
Several factors must be considered prior to constructing an insulated dog house. These considerations will influence the design, material selection, and overall effectiveness of the structure.
Size and Breed: The size of the dog house should be appropriate for the size of the dog. It should be large enough for the dog to comfortably stand, turn around, and lie down, but not so large that it becomes difficult to heat in winter. Taking accurate measurements of the dog when standing and lying down is crucial. The breed of dog is also a key factor to consider, as certain breeds are more tolerant of cold or heat than others. For instance, a short-haired breed will benefit more from insulation than a long-haired breed.
Climate: The local climate is a significant determinant of the type and amount of insulation required. In regions with harsh winters, a higher R-value insulation will be necessary to effectively retain heat. Conversely, in hotter climates, insulation helps to keep the dog house cool during the summer months. Analyzing historical temperature data for the region is helpful in determining the appropriate level of insulation.
Material Selection: The choice of materials plays a vital role in the durability, insulation, and overall effectiveness of the dog house. Common materials include wood, plastic, and metal, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Wood is a popular choice due to its natural insulating properties and aesthetic appeal. However, it requires proper treatment to prevent rot and insect infestation. Plastic is lightweight, durable, and easy to clean, but it may not provide as much insulation as wood. Metal is strong and resistant to pests, but it can conduct heat and cold readily, making it less suitable for insulated structures unless combined with effective insulation methods.
Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent the buildup of moisture and harmful gases inside the dog house. Adequate ventilation helps regulate temperature and maintain air quality, which is essential for the dog's health. Ventilation can be achieved through vents strategically placed in the walls or roof of the structure. An adjustable vent allows for controlling the airflow based on the weather conditions.
Insulation Materials and Techniques
Choosing the right insulation materials and techniques is critical for maximizing the thermal performance of the dog house. The insulation material should have a high R-value, be resistant to moisture, and be safe for the dog. Several insulation options are available, each with its own characteristics and suitability for different applications.
Rigid Foam Insulation: Rigid foam insulation, such as polystyrene or polyisocyanurate, is a popular choice for dog houses due to its high R-value and ease of installation. It is available in sheets of varying thicknesses and can be easily cut to fit the dimensions of the dog house walls, floor, and roof. Rigid foam insulation is also resistant to moisture, which is important for preventing mold and mildew growth.
Fiberglass Insulation: Fiberglass insulation is another option, although it is less commonly used in dog houses due to its potential to absorb moisture and lose its insulating properties. If using fiberglass insulation, it is essential to wrap it in a vapor barrier to prevent moisture from penetrating the material. Additionally, care should be taken to prevent the dog from accessing the fiberglass, as it can be irritating to the skin and lungs.
Reflective Insulation: Reflective insulation, such as foil-faced bubble wrap or radiant barriers, can be used to reflect radiant heat away from the dog house in summer and retain heat in winter. This type of insulation is particularly effective in climates with significant temperature fluctuations. It is typically installed on the inner or outer surfaces of the walls and roof.
Natural Insulation: Natural insulation materials, such as sheep's wool or recycled denim, are environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic insulation. These materials have good insulating properties and are naturally resistant to mold and mildew. However, they may be more expensive than other insulation options.
Insulation Techniques: Proper insulation techniques are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of the insulation material. Ensure that the insulation is installed snugly between the framing members, with no gaps or voids. Seal all seams and edges with tape or sealant to prevent air leakage. Consider insulating the floor of the dog house to prevent heat loss to the ground. The entrance to the dog house should be designed to minimize drafts, such as by using a flap or a tunnel-like entrance.
Implementing the Insulated Dog House Plan
Once the design and materials have been selected, the next step is to implement the insulated dog house plan. This involves constructing the dog house according to the design specifications and installing the insulation correctly. A systematic approach will ensure a structurally sound and effective insulated dog house.
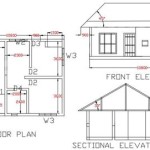
Framing: Construct a sturdy frame for the dog house using lumber that is appropriate for the size and weight of the structure. Ensure that the frame is square and level. Use galvanized nails or screws to assemble the frame. Pay attention to the placement of framing members to allow for the installation of insulation.
Exterior Sheathing: Attach exterior sheathing to the frame using plywood, OSB, or other suitable materials. This provides a solid surface for attaching the insulation and siding. Ensure that the sheathing is securely fastened to the frame and that all seams are sealed to prevent air and moisture infiltration.
Insulation Installation: Install the insulation between the framing members, ensuring that it fits snugly and that there are no gaps or voids. Secure the insulation in place with staples, adhesive, or other appropriate fasteners. If using fiberglass insulation, wrap it in a vapor barrier to protect it from moisture.
Interior Sheathing: Install interior sheathing over the insulation using plywood, OSB, or other suitable materials. This creates a finished interior surface and protects the insulation from damage. Ensure that the sheathing is securely fastened to the frame and that all seams are sealed.
Roof Construction: Construct a roof for the dog house that is sloped to allow for water runoff. Attach roofing materials, such as shingles, metal roofing, or rolled roofing, to the roof frame. Ensure that the roof is properly sealed to prevent leaks.
Finishing Touches: Add finishing touches to the dog house, such as painting or staining the exterior, adding trim, and installing a door flap or other entrance covering. Ensure that all materials used are non-toxic and safe for the dog.
Placement: The location of the insulated dog house is also a crucial factor. Place the dog house in a sheltered location, away from direct wind and rain. Position the entrance facing away from prevailing winds. In colder climates, consider placing the dog house in a sunny location to maximize solar gain. In hotter climates, place the dog house in a shaded area to minimize heat exposure.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure that the insulated dog house remains in good condition. Inspect the dog house regularly for signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or insect infestation. Repair any damage promptly to prevent further deterioration. Clean the dog house regularly to remove dirt, debris, and parasites. Replace the bedding as needed to keep it clean and dry.
By carefully considering the design, materials, and construction techniques, it is possible to create an insulated dog house that provides a comfortable and safe haven for your canine companion, protecting them from the elements year-round. A well-maintained insulated dog house will contribute significantly to the dog's overall health and well-being.

How To Build A Custom Insulated Dog House Ron Hazelton

Insulated Dog House Diy Plans

How To Build A Diy Insulated Dog House Wilker Do S

Cold Weather Dog House Plans Bradshomefurnishings Winter Insulated Diy

14 Diy Dog Houses How To Build A House Plans Blueprints

Easy Diy Winter Doghouse Self Sufficient Projects

Insulated Dog House Plans Myoutdoorplans

How To Build An Insulated Or Heated Doghouse 10 Steps

Dog House Plans Here Is Kanna Waiting For Her New Too Bad This One Isnt Houses Insulated

How To Build A Diy Insulated Dog House Wilker Do S
Related Posts