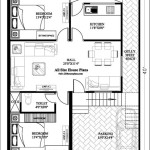
Essential Elements of a Traditional Korean House Floor Plan
Korean traditional houses, known as Hanok, are renowned for their unique architectural features that reflect the country's rich history and culture. The floor plan of a Hanok is meticulously designed to embody the principles of harmony, balance, and practicality.
The central axis of a Hanok floor plan is the "Geukgi," a raised wooden platform. The Geukgi is the most important room in the house, where the family gathers for meals and ceremonies. It is flanked by two wings, the "Sarangchae" and "Anchae." The Sarangchae, typically facing south, is the living quarters for men and guests, while the Anchae, facing north, is reserved for women and children.
The interior layout of a Hanok is characterized by its open and flowing design. Sliding doors and removable partitions allow for flexibility and adaptability, enabling the adjustment of spaces according to the needs and activities of the occupants.
Key Elements of a Traditional Korean House Floor Plan
1. Geukgi: The Geukgi is the elevated platform at the center of the house. It is raised approximately 40 centimeters above the floor and covered with warm "Ondol" flooring, a traditional underfloor heating system that provides comfort during the cold Korean winters.
2. Sarangchae: The Sarangchae is the living quarters for men and guests. It typically consists of a sitting room, a study, and a bedroom. The windows in the Sarangchae are larger than those in the Anchae, allowing for an abundance of natural light.
3. Anchae: The Anchae is the living quarters for women and children. It includes the kitchen, dining room, and bedrooms. The windows in the Anchae are smaller and face north, providing privacy and protection from the harsh southern sun.
4. Daecheong: The Daecheong is the main entrance to the house. It is a large open space that serves various functions, including receiving guests, holding ceremonies, and working. The Daecheong is typically located in the center of the house, connecting the Sarangchae and Anchae.
5. Maroo: The Maroo is a verandah or porch that surrounds the house. It is an important feature that provides additional living space, protection from the elements, and a connection to the surrounding environment. The Maroo is often used for activities such as relaxing, dining, and socializing.
6. Jangdokdae: The Jangdokdae is a platform used for storing kimchi, the staple Korean fermented dish. It is located in a cool and well-ventilated area of the house to ensure optimal preservation of the kimchi.
7. Saenghwangmun: The Saenghwangmun is a small door located at the back of the house. It is used as a secondary entrance for servants or as a private exit for women and children.
The floor plan of a traditional Korean house reflects centuries of architectural refinement and cultural heritage. The harmonious arrangement of spaces, the efficient use of natural light and ventilation, and the integration of indoor and outdoor environments create a living environment that is both practical and aesthetically pleasing.

Plan Of General Korean Traditional Hanok ホーム 建物 北欧

Popular 26 Korean Traditional House Plans Hanok

Seoul Hanok

Eugene Hanok Culture Center Dongdaemun Seoul South Korea In 2024 Traditional House Plans Korean

Drawing Of The Proposed Hanok A Floor Plan 41 B 3 D Perspective Scientific Diagram

Chapter 2 Floor Plans Of Mass Produced Hanok In Gwangju News
Ysis Of Heating Energy Reduction Wooden Based Korean Hanok Using Passive Houses Planning Package Phpp Bioresources

Cheonyeon Dong Hanok Guga Urban Architecture Archdaily

Building A Hanok In The Us Lots Of Questions Fine Homebuilding

Hanok Korean House Friendly Korea