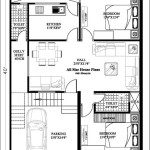
Low-Income House Plans
Finding affordable housing is a significant challenge for many individuals and families. Low-income house plans offer potential solutions by focusing on cost-effective design and construction methods. These plans aim to maximize functionality and livability while minimizing expenses, making homeownership a more achievable goal.
Several key factors contribute to the affordability of low-income housing plans. Smaller square footage is a primary consideration. Reducing the overall size of the house directly impacts material costs and labor expenses. Efficient floor plans that minimize wasted space and maximize the utility of each room also play a crucial role. Designs often prioritize open-concept layouts that combine living, dining, and kitchen areas, creating a sense of spaciousness within a smaller footprint.
Simple, straightforward designs are another hallmark of low-income house plans. Complex architectural details and elaborate rooflines add to construction costs. Therefore, these plans typically feature clean lines, basic roof shapes, and standard window and door sizes. This streamlined approach reduces material waste and simplifies the construction process, contributing to overall affordability.
Material selection is crucial in managing construction expenses. Low-income house plans often utilize readily available and cost-effective materials like concrete blocks, wood framing, and readily sourced roofing materials. These materials are typically locally available, minimizing transportation costs. Builders may also consider using alternative or recycled materials where appropriate to further reduce expenses. Careful consideration of material durability ensures long-term affordability by minimizing future repair and replacement costs.
Flexibility and adaptability are important aspects of many low-income house plans. Designs may incorporate expandable features allowing homeowners to add rooms or expand existing spaces as their needs and financial resources evolve. This flexibility proves particularly beneficial for growing families or individuals anticipating future changes in their living situations. Modular or prefabricated components can offer cost savings and faster construction times, contributing to the overall affordability and accessibility of these homes.
Energy efficiency is a critical consideration in low-income housing to minimize ongoing utility expenses. Proper insulation, energy-efficient windows, and strategically placed windows for natural light are common features in these plans. Incorporating passive solar design principles can further reduce heating and cooling costs by utilizing the sun's energy for heating and natural ventilation for cooling. These energy-saving features not only benefit homeowners financially but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
Accessibility is another important factor to consider when exploring low-income house plans. Designs should accommodate the needs of individuals with disabilities, incorporating features like wider doorways, ramps, and adaptable bathrooms. Universal design principles, which focus on creating spaces usable by people of all ages and abilities, are increasingly being incorporated into these plans, ensuring inclusivity and long-term usability.
Finding suitable low-income house plans requires thorough research. Online resources, architectural firms specializing in affordable housing, and non-profit organizations dedicated to housing assistance are valuable starting points. Working with experienced architects and builders who understand the specific challenges and opportunities of low-income housing is essential. They can help navigate local building codes, secure necessary permits, and ensure the chosen plan meets local regulations and safety standards.
Community land trusts can provide another pathway to affordable homeownership. These non-profit organizations acquire and hold land in trust, leasing it to homeowners at below-market rates. This model helps reduce the overall cost of homeownership by separating the cost of the land from the cost of the house. Exploring this option may provide additional affordability advantages for low-income individuals and families.
Government programs and subsidies can also play a significant role in making homeownership more accessible for low-income individuals and families. These programs may offer financial assistance with down payments, closing costs, or reduced mortgage rates. Thorough research and consultation with housing counselors can help potential homeowners identify and access available programs in their area. Understanding eligibility requirements and application procedures is crucial for maximizing the benefits of these programs.
Careful planning and budgeting are essential for successful low-income housing projects. Developing a realistic budget that includes all anticipated costs, from land acquisition and site preparation to material costs and labor expenses, is crucial. Working with experienced professionals can help ensure accurate cost estimations and prevent unexpected financial challenges during the construction process. Contingency planning for potential cost overruns is also recommended.

Plan 1092 National Affordable Housing Network

Est House Plans To Build Simple With Style Blog Eplans Com

10 Low Income Housing Floor Plans Ideas Tiny House Small
Floor Plan Of A Typical Low Income House Scientific Diagram

Affordable House Plans Our Est To Build Blog Homeplans Com

Building On The Affordable House Plans Of 2024 Houseplans Blog Com

10 Low Income Housing Floor Plans Ideas Tiny House Small

Est House Plans To Build Simple With Style Blog Eplans Com

Building On The Affordable House Plans Of 2024 Houseplans Blog Com

Low Income Senior Apartments One Bedroom House Plans Housing