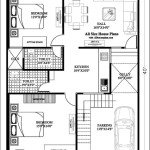
Masonry Block House Plans
Masonry block, also known as concrete masonry units (CMUs), offers a durable, cost-effective, and versatile building material for residential construction. Homes built with masonry blocks provide excellent strength, fire resistance, and energy efficiency. This article explores key considerations for those interested in masonry block house plans.
Advantages of Masonry Block Construction
Several factors contribute to the enduring popularity of masonry block in residential construction:
- Durability: Masonry block walls withstand harsh weather conditions, including high winds, heavy rain, and even seismic activity, better than many other building materials.
- Fire Resistance: CMUs are inherently fire-resistant, providing a significant safety advantage and potentially lower insurance premiums.
- Pest Resistance: Unlike wood framing, masonry block is not susceptible to damage from termites or other pests.
- Energy Efficiency: The thermal mass of concrete blocks helps regulate indoor temperatures, reducing heating and cooling costs.
- Soundproofing: The density of CMUs provides excellent sound insulation, creating a quieter living environment.
- Design Versatility: Masonry blocks can be used to create a variety of architectural styles, from traditional to contemporary.
Planning a Masonry Block House
Careful planning is essential for a successful masonry block construction project. The following points should be addressed during the planning phase:
- Budget: While generally cost-effective, the final cost of a masonry block home depends on factors like size, design complexity, and labor costs in the specific region.
- Site Selection and Preparation: A proper foundation is crucial for supporting the weight of masonry walls. Soil conditions and topography must be considered when selecting a building site.
- Design and Layout: Masonry block lends itself to a variety of designs, but careful consideration must be given to wall placement, window and door openings, and roof design.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Local building codes dictate specific requirements for masonry block construction, including wall thickness, reinforcement, and mortar specifications. Compliance with these codes is mandatory.
Types of Masonry Blocks
Several types of masonry blocks are available, each with its own characteristics and applications:
- Hollow Core Blocks: The most common type, offering a balance of strength, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation. The hollow cores can be filled with insulation for increased energy efficiency.
- Solid Blocks: Provide maximum strength and sound insulation, typically used for structural elements like foundation walls.
- Decorative Blocks: Available in various shapes, textures, and colors, allowing for aesthetic customization of exterior and interior walls.
- Split-Face Blocks: Offer a textured, stone-like appearance, often used for exterior facades.
Construction Techniques
Building with masonry block requires specialized skills and tools. Key aspects of the construction process include:
- Laying the Blocks: Blocks are laid in a staggered pattern and joined with mortar. Proper mortar consistency and jointing techniques are essential for structural integrity.
- Reinforcement: Steel reinforcing bars (rebar) are often placed within the block cores and grouted to enhance the wall's strength and resistance to cracking.
- Lintels and Jambs: Precast concrete lintels and jambs are used to span door and window openings.
- Wall Finishes: Masonry block walls can be finished with various materials, including stucco, plaster, paint, or veneer.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Maximizing energy efficiency in a masonry block home is a crucial consideration. Several methods can be employed:
- Core Filling: Filling the hollow cores of the blocks with insulation material like vermiculite or foam significantly improves thermal performance.
- Exterior Insulation: Applying rigid insulation board to the exterior of the walls and covering it with a finish material creates a continuous insulation layer.
- Interior Insulation: Applying insulation to the interior walls, although less common, can also improve energy efficiency.
Maintenance and Durability
Masonry block homes are known for their low maintenance requirements. However, some periodic maintenance is necessary to ensure long-term durability:
- Mortar Joint Inspection: Regularly inspect mortar joints for cracks or deterioration and repair as needed to prevent water infiltration.
- Cleaning: Periodic cleaning with a mild detergent and water can remove dirt and grime buildup.
- Sealing: Applying a sealant to exterior walls can help protect against moisture penetration and staining.
Finding Masonry Block House Plans
A variety of resources are available for finding masonry block house plans:
- Architects and Designers: Working with an architect or designer allows for customization and ensures the plans meet specific needs and local building codes.
- Online Plan Resources: Numerous websites offer a wide selection of pre-designed masonry block house plans.
- Builders and Contractors: Many builders specializing in masonry construction have access to house plans or can recommend architects and designers.
Choosing the right masonry block house plan requires careful consideration of various factors, including budget, design preferences, local climate, and building codes. Thorough planning and collaboration with experienced professionals are essential for a successful project.

Cool Energy Efficient Concrete House Plans Houseplans Blog Com

Cool Energy Efficient Concrete House Plans Houseplans Blog Com

Concrete House Plans That Provide Great Value And Protection
Concrete Block Icf Design Home 1 Bdrm Bath 550 Sq Ft Plan 132 1488

Cool Energy Efficient Concrete House Plans Houseplans Blog Com

Concrete House Plans Sater Design Collection

Concrete Block House Globmac
Building A Cinder Block House Home Builders In Chicago Il

Concrete House Plans Icf And Block Modern Home
Concrete Block Icf Design Home 4 Bdrm 3 Bath 2024 Sq Ft Plan 132 1257