My House Floor Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
A house floor plan serves as a fundamental blueprint, dictating the spatial arrangement and overall functionality of a dwelling. It is a two-dimensional representation of a house, viewed from above, illustrating the relationships between rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other fixed features. Understanding and effectively utilizing a floor plan is crucial, whether constructing a new home, renovating an existing one, or simply exploring potential living spaces.
The creation and interpretation of house floor plans involve a blend of architectural principles, spatial reasoning, and practical considerations. Accuracy and detail are paramount, as the floor plan directly impacts the construction process, interior design choices, and the inhabitants' lived experience within the home.
The purpose of a floor plan extends beyond mere visual representation. It acts as a communication tool, facilitating collaboration between architects, builders, interior designers, and homeowners. It allows for the visualization of the final product, identification of potential problems, and optimization of space utilization before any physical construction commences. A well-designed floor plan contributes significantly to the comfort, efficiency, and aesthetic appeal of a house.
Key Elements of a House Floor Plan
Several key elements are consistently present in a comprehensive house floor plan. These elements provide the necessary information for accurate interpretation and effective utilization.
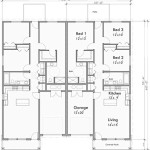
Walls: Walls are represented by solid lines, typically thicker than other lines on the plan. Exterior walls are usually drawn thicker than interior walls to distinguish them. The walls delineate the enclosed spaces of the house and provide structural support.
Doors and Windows: Doors are depicted as openings in the walls with an arc indicating the swing direction. The size of the door is also usually indicated. Windows are represented by two or more parallel lines within the wall, depicting the window frame and glazing. The placement and size of doors and windows are critical for controlling access, ventilation, and natural light.
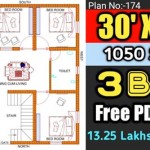
Rooms: Rooms are the labeled areas within the house, representing the intended function of each space (e.g., living room, bedroom, kitchen, bathroom). The dimensions of each room are usually indicated, providing information about its size and shape. Accurate room dimensions are essential for furniture placement and space planning.
Stairs: Stairs are represented by a series of lines indicating the steps, with an arrow showing the direction of ascent. The number of risers (vertical steps) is often noted, as well as the overall dimensions of the staircase. Stairs are critical components for multi-story homes, requiring careful consideration of safety and accessibility.
Fixtures and Appliances: Fixed fixtures, such as toilets, sinks, bathtubs, and built-in cabinets, are represented by symbols or scaled drawings to indicate their position and size. Similarly, major appliances like refrigerators, stoves, and washing machines may be included. The placement of fixtures and appliances significantly impacts the functionality of kitchens and bathrooms.
Dimensions and Measurements: Dimensions are crucial for accurately representing the size and proportions of the house. They are typically indicated using lines and numbers, showing the length, width, and height of rooms, walls, and other features. Accurate dimensions are essential for construction and for planning interior layouts.
Scale: Every floor plan includes a scale that indicates the relationship between the drawing and the actual size of the house. Common scales include 1/4 inch = 1 foot or 1/8 inch = 1 foot. The scale allows for the accurate measurement of distances and areas on the plan.
North Arrow: A north arrow indicates the orientation of the house relative to the cardinal directions. This is important for understanding the direction of sunlight and wind exposure, which can affect the energy efficiency and comfort of the house.
Types of House Floor Plans
House floor plans can be categorized into several types, based on their level of detail, purpose, and the stage of the design process they represent.
Conceptual Floor Plan: This is a preliminary sketch that explores different spatial arrangements and design ideas. It is typically less detailed than other types of floor plans and focuses on the overall layout and relationships between spaces. Conceptual floor plans are used to generate and evaluate design alternatives early in the design process.
Schematic Floor Plan: This type of plan expands on the conceptual floor plan, adding more detail and refining the layout. It includes approximate dimensions, the location of doors and windows, and the arrangement of major rooms. Schematic floor plans provide a clearer picture of the overall design and serve as a basis for further development.
Detailed Floor Plan: This is a highly detailed plan that includes all the information necessary for construction. It shows the exact dimensions of walls, rooms, doors, windows, and fixtures. It also includes notes and specifications about materials, finishes, and construction methods. Detailed floor plans are used by builders, contractors, and other construction professionals to accurately construct the house.
As-Built Floor Plan: This type of plan is created after the house has been constructed. It reflects any changes or modifications that were made during the construction process. As-built floor plans are valuable for future renovations or repairs, as they provide an accurate record of the existing conditions of the house.
3D Floor Plan: This type of plan provides a three-dimensional representation of the house, allowing for a more realistic visualization of the space. 3D floor plans can be created using computer-aided design (CAD) software and are often used for marketing or presentation purposes.
Reading and Interpreting a House Floor Plan
Effectively reading and interpreting a house floor plan requires a systematic approach and an understanding of the symbols and conventions used.
Orient Yourself: Begin by identifying the north arrow to understand the orientation of the house. This will help you visualize the direction of sunlight and wind exposure.
Identify the Walls: Locate the solid lines representing the walls. Note the thickness of the walls, as this indicates whether they are exterior or interior walls.
Locate Doors and Windows: Identify the symbols representing doors and windows. Pay attention to the swing direction of the doors and the size and type of windows.
Identify Rooms and Their Functions: Read the labels indicating the function of each room (e.g., living room, bedroom, kitchen, bathroom). Consider the relationships between the rooms and how they flow together.
Examine Dimensions and Measurements: Review the dimensions and measurements to understand the size and proportions of the rooms and other features. Use the scale to accurately measure distances and areas on the plan.
Identify Fixtures and Appliances: Locate the symbols representing fixed fixtures and appliances. Consider their placement and how they will affect the functionality of the spaces.
Visualize the Space: Use the floor plan to visualize the three-dimensional space of the house. Imagine yourself walking through the rooms and consider how the layout will work for your needs and lifestyle.
Consider the Circulation: Analyze the flow of movement through the house. Consider how people will move from room to room and how the layout will affect privacy and noise levels.
Identify Potential Problems: Look for potential problems or areas for improvement. Consider whether the layout is efficient, whether there is enough storage space, and whether the design meets your needs and budget.
Ultimately, a house floor plan is a vital tool for designing, constructing, and understanding a home. Its ability to communicate spatial information effectively makes it indispensable for architects, builders, and homeowners alike. A thorough understanding of floor plan elements, types, and interpretation techniques enhances the ability to create functional, aesthetically pleasing, and comfortable living spaces.

Floor Plans Types Symbols Examples

Pin On House Layout

Changing The Layout Of My House Houzz

My Ideal House Floor Plan Plans Courtyard Simple

My Home Free Design 3d House Floor Plans By Planner 5d

My Dream Home Free Design 3d Floor Plans By Planner 5d

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

How Do I Get A Floor Plan For My Property
My Top 6 Floor Plan Features Houseplans Blog Com

My Dream House Free Design 3d Floor Plans By Planner 5d