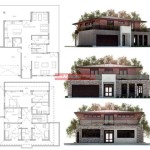
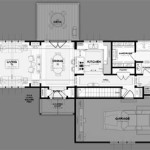
Essential Aspects of Passive Solar House Floor Plans
Harnessing sunlight to create a comfortable and energy-efficient home is the heart of passive solar design. Designing a passive solar house involves carefully considering floor plans to maximize solar energy gain and minimize heat loss, resulting in lower energy costs and a more sustainable living environment.
1. Orientation
The most fundamental aspect of passive solar floor plans is their orientation to the sun. Ideally, the home should be positioned with its front facade facing south in the Northern Hemisphere or north in the Southern Hemisphere. This alignment ensures maximum exposure to direct sunlight during winter months when additional heating is needed.
2. Thermal Zones
Passive solar floor plans are typically divided into thermal zones based on their function and sunlight exposure. The "warm zone" includes the living room, kitchen, and other rooms that should be the most comfortable. It is positioned in the southern or northern part of the house to receive the most daylight. The "cool zone" includes bedrooms and bathrooms, which are typically located on the north side of the house and require less heat.
3. Windows and Glass Doors
Windows and glass doors act as the conduit for sunlight to enter the home. South-facing windows should be large and plentiful to maximize solar gain. The windows should be double- or triple-glazed with low-emittance (Low-E) coatings to minimize heat loss. Overhangs or awnings can be used to shade windows during summer months to prevent overheating.
4. Thermal Mass
Thermal mass refers to the ability of materials to store heat. Passive solar house floor plans incorporate thermal mass materials, such as concrete, stone, or tiles, into their design. These materials absorb heat during the day and release it at night, helping to stabilize indoor temperatures.
5. Insulation and Air Sealing
While windows and thermal mass allow for the exchange of heat, it's equally crucial to prevent heat loss through air infiltration. Passive solar floor plans include thorough insulation throughout the building envelope, focusing on walls, ceilings, and floors. Air sealing measures, such as caulk and weatherstripping, minimize drafts and improve the home's overall energy efficiency.
6. Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation strategies, such as cross-ventilation and stack effect, can be incorporated into passive solar house floor plans to reduce the need for mechanical cooling. Cross-ventilation involves placing windows on opposite sides of a room or the house to allow for air movement. The stack effect takes advantage of the natural tendency of warm air to rise, creating airflow through open windows or vents at different heights.
7. Sunrooms and Conservatories
Sunrooms or conservatories are enclosed spaces that are designed to maximize solar gain. They typically feature large windows or skylights on the south side, allowing sunlight to enter and heat the space. Sunrooms can be used as passive solar heaters, warming the adjoining rooms in winter months.
By carefully considering these essential aspects, passive solar house floor plans can create comfortable, energy-efficient homes that rely less on mechanical systems for heating and cooling.
Ranch House Plans For A Passive Solar 1 Bedroom Home

Great Floor Plan For Solar Passive Home In Google Search House Plans Narrow

Passive Solar House Design

Passive Solar House Plans Version 3 Byexample Com

Passive Solar Home Plan At Alternative Heating Com House Design Homes Plans

Solar Adobe House Plan 1870
What Does A Passive House Cost To Build Leanhaus

Passive Solar Plans Unique Energy Efficient Hillside Home

Passive Solar House Plans For Our Off Grid Homestead Byexample Com

Passive Solar 1600 0060