The Plan of a Residential House: A Comprehensive Guide
Planning a residential house is a complex undertaking that requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure a functional, aesthetically pleasing, and budget-friendly dwelling. A well-thought-out house plan serves as a blueprint for construction, guiding the entire process from foundation to finishing touches. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the essential components of a residential house plan.
1. Site Analysis and Planning
The first step in planning a residential house is to conduct a thorough site analysis. This involves assessing the physical characteristics of the land, including its topography, soil type, and access points. The analysis also considers surrounding factors such as zoning regulations, utility availability, and proximity to amenities.
Based on the site analysis, the architect or designer develops a preliminary site plan, outlining the location of the house on the property and its orientation relative to sunlight and prevailing winds. This plan also includes the placement of other elements such as driveways, garages, patios, and landscaping.
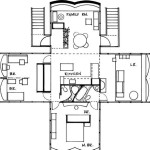
2. Floor Plan Design
The floor plan is the most crucial component of a residential house plan, illustrating the layout of rooms, their sizes, and their connections. It is essential to carefully consider the functional needs of the household members, their lifestyles, and their spatial requirements. The floor plan should ensure a smooth flow of movement throughout the house, with adequate space for daily activities.
Common areas such as living rooms, dining rooms, and kitchens are typically situated centrally for easy access and social interaction. Bedrooms are usually grouped together for privacy and comfort. Bathrooms are typically located near bedrooms or shared spaces, while utility rooms and laundry areas are often placed in less visible locations.
3. Elevation and Section Drawings
Elevation drawings are visual representations of the exterior facades of the house, showing its height, shape, and the arrangement of windows, doors, and other architectural features. These drawings help visualize the overall aesthetic appeal of the house and ensure consistency in its design.
Section drawings are cross-sectional views that illustrate the internal structure of the house, revealing the placement of walls, floors, ceilings, and other structural components. These drawings are vital for understanding the building's construction methods and ensuring adequate support for the various elements.
4. Building Systems and Specifications
The house plan should include detailed specifications for all building systems, including the electrical, plumbing, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), and fire suppression systems. These specifications ensure that the systems are installed correctly and safely, meeting all applicable building codes.
The plan should also outline the materials to be used for construction, including the type of foundation, framing, roofing, siding, windows, doors, and finishes. This information is crucial for contractors to bid on the project accurately and ensure consistent quality throughout the construction process.
5. Green Building Considerations
In today's environmentally conscious world, it is imperative that house plans incorporate sustainable design principles. This involves considering energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of environmentally friendly materials. By incorporating green building features such as solar panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and energy-efficient appliances, homeowners can reduce their environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
For instance, the house plan can include provisions for maximizing natural light and ventilation to minimize reliance on artificial lighting and air conditioning. This can be achieved through strategically placed windows, skylights, and shaded porches.
6. Safety and Accessibility
A well-designed house plan prioritizes the safety and accessibility of its occupants. The plan should include features that enhance safety such as smoke detectors, fire sprinklers, carbon monoxide detectors, and adequate emergency exits. For accessibility, the plan should consider the needs of individuals with disabilities, ensuring smooth movement and access to all areas of the house.
This may involve incorporating ramps, wider doorways, accessible bathrooms, and other features that promote inclusivity and allow all residents to live comfortably and safely.
7. Flexibility and Adaptability
It is beneficial to incorporate elements of flexibility and adaptability into the house plan, considering the possibility of future modifications or changes in lifestyle. Open-plan layouts can offer greater flexibility, allowing for reconfiguration as needs evolve. The plan may also include provisions for future additions or expansions, ensuring the house can adapt to changing family sizes and needs.
This future-proofing approach allows the house to remain functional and relevant for years to come, ensuring its longevity and value.

Simple Floor Plans Qdhl7 Home Design House Tiny

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

Small House Design 2024001 Pinoy Eplans Floor Plans

Typical Floor Plan Small Apartment Building Residential

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan
How To Do A Floor Plan For Residential Quora

Diffe Types Of Residential Building Plans And Designs First Floor Plan House Design

Residential House Floor Plan Best Floorplan Architectural Hire A Make My Expert

41 X30 Ground Floor Office Cum Residential House Plan Is Given In This Autocad Model Now Cadbull

Typical Plan View Of A Multistoried Four Storied Residential Building Scientific Diagram