Plans for Tiny Homes on Wheels
The rising popularity of tiny homes on wheels reflects a growing desire for affordable housing, sustainable living, and increased mobility. Careful planning is crucial for maximizing space utilization and ensuring the tiny home meets specific needs and lifestyle preferences. This article explores key considerations when developing plans for a tiny home on wheels.
Choosing the Right Trailer
The foundation of any tiny home on wheels is the trailer. Factors to consider include weight capacity, length, and width. The trailer's weight capacity dictates the overall weight of the finished tiny home, including appliances, furniture, and personal belongings. Longer trailers offer more living space but can impact maneuverability. Width restrictions vary by state, and exceeding these limits can complicate transportation. Researching local regulations and considering potential travel routes helps determine the suitable trailer dimensions. Steel trailers are robust and offer excellent durability, while aluminum trailers are lighter, potentially increasing fuel efficiency.
Designing the Layout
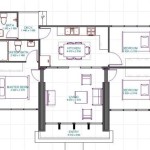
Effective space planning is paramount in tiny home design. Every square foot must serve a purpose. Prioritizing needs and desired features helps determine the optimal layout. Key questions to address include sleeping arrangements, kitchen size and functionality, bathroom necessities, and storage solutions. Loft spaces can efficiently utilize vertical space for sleeping areas, freeing up valuable floor space below. Multifunctional furniture, such as convertible sofas or tables with built-in storage, maximizes space efficiency. Incorporating ample natural light and ventilation enhances the perception of spaciousness and contributes to a comfortable living environment.
Addressing Utilities and Systems
Tiny homes on wheels require carefully planned utility systems for water, electricity, and waste management. Water tanks need to be sized appropriately for usage needs, and a water heater should be selected based on energy efficiency and available space. Electrical systems must comply with safety regulations and provide sufficient power for appliances and lighting. Options include connecting to shore power or utilizing solar panels for off-grid capabilities. Waste management solutions typically involve composting toilets and greywater systems. Understanding the specific requirements for each system is crucial for ensuring functionality and compliance with local regulations.
Material Selection and Construction
Choosing durable and lightweight materials is vital for tiny home construction. Structural integrity, insulation, and weather resistance are critical considerations. Common framing materials include wood studs, steel framing, and structural insulated panels (SIPs). SIPs offer superior insulation and structural strength, contributing to energy efficiency and overall durability. Exterior siding options include wood, metal, and composite materials, each with varying levels of maintenance and weather resistance. Roofing materials should be lightweight and durable, capable of withstanding various weather conditions. Proper insulation is essential for regulating temperature and minimizing energy consumption.
Compliance with Regulations
Navigating regulations for tiny homes on wheels varies significantly by location. Some jurisdictions classify them as recreational vehicles (RVs), while others have specific building codes for tiny homes. Researching local zoning ordinances, building codes, and permitting requirements is crucial before beginning construction. Understanding the specific regulations regarding size, weight, utilities, and parking ensures compliance and avoids potential legal complications. Addressing these regulatory aspects early in the planning process streamlines the building process and facilitates a smooth transition into tiny home living.
Budgeting and Financing
Developing a realistic budget is essential for a successful tiny home project. Costs can vary widely depending on the size, materials, and complexity of the design. Factor in expenses for the trailer, materials, appliances, labor (if not building yourself), and permits. Exploring financing options, such as personal loans or specialized tiny home loans, can help manage the financial aspect of the project. Creating a detailed budget and tracking expenses throughout the building process helps stay within financial constraints and ensures the project's feasibility.
Maintenance and Longevity
Planning for maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity of a tiny home on wheels. Regular inspections and preventative maintenance tasks, such as cleaning gutters, checking seals, and maintaining appliances, help prevent costly repairs and extend the lifespan of the home. Choosing durable materials and employing proper construction techniques contribute to the overall resilience and longevity of the structure. Considering the long-term maintenance requirements during the planning phase helps ensure the tiny home remains a comfortable and functional living space for years to come.

Tiny House Floor Plans 32 Home On Wheels Design

Escape Traveler A Tiny House On Wheels That Comfortably Sleeps 6 Floor Plans Trailer

Tiny House Floor Plans 32 Long Home On Wheels Design

Design A Tiny House On Wheels Tips And Tools For Diyers

224 Sq Ft Tiny House On Wheels By Living Homes Small Diy Floor Plans

Tiny House Plans The Project

Free Tumbleweed Diy Tiny House Plans Houses

How To Pick The Best Tiny House On Wheels Floor Plan Wayward Home

27 Adorable Free Tiny House Floor Plans Craft Mart

Floor Plans For Your Tiny House On Wheels Photos