Essential Aspects of Slab Foundation House Plans
When building a home, selecting the right foundation type is crucial. Slab foundations are a popular choice due to their cost-effectiveness, durability, and ease of construction. If you're planning on building a home with a slab foundation, it's important to have a well-designed plan that incorporates the essential aspects.
1. Soil Conditions
The soil on which the slab foundation will be built plays a vital role in its design. The soil should be stable and well-drained to prevent settling and cracking of the foundation. If the soil is not suitable, additional measures such as soil stabilization or a thickened slab may be necessary.
2. Concrete Thickness and Reinforcement
The thickness and reinforcement of the concrete slab are crucial for its strength and durability. The thickness of the slab will depend on the load-bearing requirements of the structure. The concrete should be reinforced with rebar or wire mesh to resist cracking and provide structural integrity.
3. Drainage System
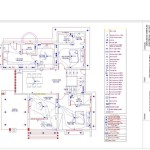
Proper drainage is essential to prevent water from seeping into the foundation and causing damage. The slab should be sloped away from the house to allow rainwater to drain off. Additionally, a perimeter drain system may be installed to collect and redirect water.
4. Vapor Barrier
A vapor barrier should be installed below the concrete slab to prevent moisture from rising from the ground into the house. This barrier will help to protect the interior from mold, mildew, and other moisture-related issues.
5. Expansion Joints
Expansion joints are placed in the concrete slab to allow for movement due to temperature changes and shrinkage. These joints prevent the slab from cracking and provide flexibility.
6. Plumbing and Electrical Conduits
All plumbing and electrical lines should be carefully planned and installed before pouring the concrete slab. Conduits or sleeves should be provided to allow for these lines to pass through the slab.
7. Insulation
Insulating the slab foundation can help to reduce energy costs and improve the comfort level of the home. Insulation materials such as polystyrene or rigid foam can be placed below or on top of the concrete.
Conclusion
By considering these essential aspects in your slab foundation house plans, you can ensure a strong, stable, and durable foundation for your home. Proper planning and execution will help to prevent future problems and provide a safe and comfortable living space for many years to come.

Foundation Plans How To Choose The Right One Houseplans Blog Com

Foundation Layout

Foundation Plans How To Choose The Right One Houseplans Blog Com

Civil Engineering 12 24 11 Architectural House Plans How To Plan Floor Layout

Pin On Javítás

Foundation Plans How To Choose The Right One Houseplans Blog Com

House Plans With Slab Foundation

House Plans With Slab Foundation

European House Plan With Slab Foundation 1889

Foundation Plans How To Choose The Right One Houseplans Blog Com