Tornado Safe House Plans: Understanding Shelter Options for Enhanced Safety
Tornadoes pose a significant threat in many regions, necessitating robust safety measures to protect individuals and families. A crucial aspect of preparedness is having access to a designated shelter, ideally a tornado safe room or underground storm shelter. These structures are designed to withstand the extreme forces generated by tornadoes, providing a critical refuge during severe weather events. This article explores various tornado safe house plans, examining the features, construction requirements, and suitability of different shelter options.
The purpose of a tornado safe room or storm shelter is to provide near-absolute protection from the impact of a tornado. This means the structure must be capable of resisting winds exceeding 250 mph and impacts from debris traveling at high velocities. To achieve this level of protection, specific design and construction standards must be followed. These standards are often based on guidelines established by organizations like the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) and the International Code Council (ICC).
Selecting the appropriate tornado safe house plan depends on several factors, including the available space, budget constraints, the number of occupants, and the specific risks associated with the geographical location. Considering these factors is crucial in ensuring the chosen shelter provides adequate protection and meets the needs of its users.
Key Considerations for Tornado Safe House Plans
Before selecting a specific plan, several key aspects must be addressed to ensure the shelter meets the required safety standards and is appropriately sized for its intended use. These considerations are fundamental to the effectiveness of the shelter and should be carefully evaluated during the planning phase.
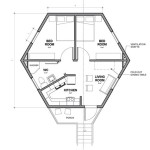
First, the location of the shelter is of paramount importance. It should be readily accessible from all areas of the home or building. Ideally, the shelter should be located on the lowest floor, preferably within a basement or crawlspace. If an above-ground shelter is necessary, it should be situated in a central room away from exterior walls and windows. The proximity of the shelter to sleeping areas and high-traffic zones is essential for quick and easy access during a tornado warning.
Second, the size of the shelter must be sufficient to accommodate all occupants comfortably for an extended period. FEMA provides guidelines on the minimum square footage required per person, typically around 3 square feet. However, it's advisable to provide additional space for supplies, seating, and mobility. Overcrowding can lead to discomfort and anxiety during a stressful situation, diminishing the shelter's effectiveness.
Third, ventilation is a critical aspect of storm shelter design. While sealing the shelter to prevent debris intrusion is important, adequate ventilation is necessary to prevent carbon dioxide buildup and maintain breathable air quality. Ventilation systems should be designed to resist tornado-force winds and prevent water ingress. Incorporating a passive ventilation system or a battery-operated fan can help ensure a continuous supply of fresh air.
Types of Tornado Safe House Plans
Several types of tornado safe house plans are available, each offering varying levels of protection and suitability for different situations. These plans can be broadly categorized into underground shelters, above-ground safe rooms, and reinforced interior rooms.
Underground shelters, typically constructed of reinforced concrete or steel, offer the highest level of protection. These shelters are buried beneath the ground, providing a direct barrier against wind and debris. The entrance to the shelter is usually protected by a heavy steel door and a reinforced hatch. Underground shelters are particularly well-suited for areas with a high risk of tornadoes, as they offer complete protection from the storm's destructive forces.
Above-ground safe rooms are typically constructed within an existing building, such as a home or office. These rooms are designed to withstand tornado-force winds and debris impacts. They are typically reinforced with steel and anchored to the foundation of the building. Above-ground safe rooms provide a convenient shelter option, as they can be integrated into the existing structure without requiring extensive excavation. However, they may offer slightly less protection than underground shelters, as they are still subject to the structural integrity of the surrounding building.
Reinforced interior rooms involve strengthening an existing interior room of a building to provide a degree of protection from tornadoes. This typically involves reinforcing the walls, ceiling, and door with steel and anchoring them to the foundation. While this option is less expensive than constructing a dedicated safe room or underground shelter, it also offers a lower level of protection. Reinforced interior rooms are best suited for situations where the risk of tornadoes is relatively low, or as a temporary shelter while seeking a more substantial refuge.
Each of these shelter types requires adherence to specific construction standards and guidelines to ensure their effectiveness. These standards address aspects such as wall construction, door and window protection, and anchoring to the foundation.
Key Features and Construction Requirements
Regardless of the specific type of tornado safe house plan chosen, certain key features and construction requirements are essential for ensuring the shelter's structural integrity and protective capabilities. These elements are critical to the shelter's ability to withstand the forces generated by a tornado.
One of the most important features is the structural integrity of the walls, floor, and roof. These components must be capable of withstanding extreme wind pressures and impacts from debris. Walls are typically constructed of reinforced concrete, steel, or a combination of materials. The reinforcement should be adequate to resist the bending and shear forces generated by the wind. The floor and roof must also be similarly reinforced to prevent collapse under load. Connections between the walls, floor, and roof must be strong and properly anchored to ensure the entire structure acts as a single unit.
The door and any windows are also critical components of the shelter's design. The door must be a heavy-duty steel door with multiple locking points to prevent it from being blown open during a tornado. Windows, if present, should be small and constructed of impact-resistant glass or covered with steel shutters. The door and windows should be designed to withstand debris impacts and prevent water intrusion.
Anchoring the shelter to the foundation is essential for preventing it from being lifted or displaced by the wind. Anchoring systems typically involve using steel anchors embedded in the foundation and connected to the walls of the shelter. The anchors should be spaced appropriately and designed to resist the uplift forces generated by the tornado. Proper anchoring is particularly important for above-ground safe rooms, as they are more vulnerable to being lifted or overturned by the wind.
In addition to these structural requirements, other features can enhance the safety and comfort of the shelter. These include ventilation systems, emergency supplies, communication devices, and first-aid kits. Proper lighting is also essential for navigating the shelter during a power outage. A well-equipped shelter can significantly improve the experience of occupants during a stressful situation.
Finally, it's imperative that the construction of any tornado safe house plan is carried out by qualified professionals who are experienced in building tornado-resistant structures. This ensures that the shelter is built according to the prescribed standards and that all components are properly installed and connected. A properly constructed shelter provides the best possible protection from the destructive forces of a tornado.

Q4 Architects Tornado Proof Home Is An Indestructible House Within A

First Floor Plan Of Tornado Proof House By Q4 Team Source Scientific Diagram

An Ingenious Home Built To Battle Tornadoes Bloomberg
Shelter From The Storm Builder

An Ingenious Home Built To Battle Tornadoes Bloomberg

Safe Room Construction With Insulated Concrete Forms Tornado Planning
10 Design Architecture S Tornado Proof Home

Tornado Proof House 10 Design

How To Build An Above Ground Storm Shelter Part 1 Shelters Tornado

Fema Approved Safe Rooms Provide Additional Protection From Natural Disasters Liteform