Vaulted Ceilings House Plans: Enhancing Space and Light
Vaulted ceilings, also known as cathedral ceilings, represent a significant design element in architectural planning. They offer visual appeal and functional advantages, creating a sense of spaciousness and enhancing natural light distribution within a home. This article explores the considerations involved in selecting house plans that incorporate vaulted ceilings, covering various styles, structural implications, and energy efficiency aspects.
The term “vaulted ceiling” encompasses a range of designs where the ceiling rises above the standard flat plane. This elevation can be achieved through various structural techniques, resulting in different aesthetics. From simple angled ceilings to more complex arched or domed structures, the choice of vaulted ceiling design profoundly impacts the overall character of the house.
House plans featuring vaulted ceilings are increasingly popular due to the perception of increased volume and the aesthetic enhancement they provide. The design process requires careful planning to ensure structural integrity, energy efficiency, and overall harmony with the architectural style of the house. Understanding the nuances of vaulted ceiling design is crucial for homeowners seeking to incorporate this feature into their living spaces.
Types of Vaulted Ceilings
Several distinct types of vaulted ceilings exist, each with unique characteristics and construction methods. The selection of a specific type significantly influences the interior design and structural requirements of the house. A clear understanding of these types allows for a more informed decision during the house planning phase.
The *Cathedral Ceiling* is perhaps the most common type. It typically features two equal, sloping sides that meet at a central ridge, forming a symmetrical triangular shape. This design is straightforward to construct and offers a clean, uncluttered aesthetic. Cathedral ceilings are often used in living rooms, great rooms, and master bedrooms to create a sense of grandeur.
A *Gable Vaulted Ceiling* is similar to a cathedral ceiling but usually follows the roofline of a gable roof. The slope of the ceiling mirrors the slope of the roof, creating a cohesive and visually appealing design. Gable vaulted ceilings can be incorporated into various architectural styles, from traditional to modern.
*Arched Vaulted Ceilings* introduce a curved element into the design. These ceilings can range from gentle curves to more pronounced arches, adding a touch of elegance and sophistication. Construction of arched ceilings is more complex than flat or angled ceilings, requiring specialized framing techniques.
*Domed Ceilings* represent a more elaborate form of vaulted ceiling. They create a focal point within a room and are often found in larger, more formal spaces. Domed ceilings require significant structural support and are generally more expensive to construct.
*Shed Vaulted Ceilings* feature a single sloping plane, creating a more asymmetrical design. These ceilings are often used in modern or contemporary homes to add visual interest and maximize natural light. The angle of the slope can be varied to create different effects.
Regardless of the specific type, the choice of vaulted ceiling should complement the overall architectural style of the house and meet the homeowner's aesthetic preferences. Careful consideration of the structural implications and energy efficiency aspects is also essential.
Structural Considerations for Vaulted Ceilings
The construction of vaulted ceilings introduces unique structural challenges compared to standard flat ceilings. The removal of horizontal ceiling joists, which typically provide lateral support to exterior walls, necessitates alternative methods to maintain the structural integrity of the building. Proper engineering and construction techniques are crucial to prevent wall movement and ensure the long-term stability of the house.
One of the primary concerns is *wall racking*, which refers to the tendency of walls to lean or skew under lateral loads, such as wind or seismic forces. In houses with vaulted ceilings, the absence of ceiling joists reduces the resistance to wall racking. To compensate, structural engineers often specify the use of shear walls, which are designed to resist lateral forces. Shear walls are typically constructed with plywood or other rigid sheathing materials and are strategically placed throughout the house to provide adequate support.
Another important consideration is the *transfer of loads* from the roof to the foundation. Vaulted ceilings can alter the load distribution, potentially increasing the stress on certain structural elements. The design must account for these changes and ensure that the foundation is adequately sized to support the increased loads.
The *framing materials* used in the construction of vaulted ceilings must also be carefully selected. Larger spans may require the use of engineered lumber, such as laminated veneer lumber (LVL) or parallel strand lumber (PSL), which offers higher strength and stiffness compared to traditional lumber. The size and spacing of rafters or trusses must also be determined based on the specific design and local building codes.
The *connection details* between the roof framing and the walls are critical for ensuring structural integrity. Proper fastening techniques, such as the use of metal connectors and adequately sized fasteners, are essential to prevent the roof from separating from the walls under load. Regular inspections during the construction process are recommended to verify that all structural elements are installed correctly.
In some cases, *tie beams* or *collar ties* may be required to provide additional lateral support. Tie beams are horizontal members that connect opposing walls, while collar ties are horizontal members that connect opposing rafters. These elements help to resist outward thrust from the roof and prevent wall movement. The need for tie beams or collar ties depends on the specific design and the magnitude of the lateral loads.
Therefore, incorporating vaulted ceilings into house plans entails a detailed structural analysis and careful implementation during construction. This necessitates collaboration between architects, engineers, and builders to ensure a structurally sound and safe living environment.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Vaulted ceilings can present challenges to energy efficiency due to the increased surface area exposed to the exterior environment and the potential for heat loss or gain. The effectiveness of insulation and ventilation strategies plays a crucial role in mitigating these issues and maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures while minimizing energy consumption. Addressing these factors from the planning stage is key to achieving an energy-efficient home with vaulted ceilings.
Effective *insulation* is paramount in minimizing heat transfer through the ceiling. The type and thickness of insulation should be carefully selected based on the climate zone and the orientation of the house. Common insulation materials include fiberglass batts, cellulose, spray foam, and rigid foam boards. Spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing capabilities, which can significantly reduce energy loss. Rigid foam boards can be used in conjunction with other insulation materials to further enhance thermal performance.
*Ventilation* is also crucial to prevent moisture buildup and maintain a healthy indoor environment. Proper ventilation helps to remove warm, moist air from the ceiling cavity, preventing condensation and potential damage to the structure. Ridge vents and soffit vents are commonly used to provide natural ventilation. Powered ventilation systems can also be used to enhance airflow, especially in hot and humid climates.
The *orientation* of the house can significantly impact energy efficiency. Vaulted ceilings facing south or west may receive more direct sunlight, potentially leading to excessive heat gain in the summer. Overhangs, awnings, or strategically placed trees can help to shade the ceiling and reduce heat gain. Windows placed in vaulted ceilings should be energy-efficient, with low-E coatings to minimize heat transfer.
*Air sealing* is essential to prevent air leakage through cracks and gaps in the ceiling. Air leakage can significantly increase energy consumption and reduce the effectiveness of insulation. Sealing around penetrations for electrical wiring, plumbing, and lighting fixtures is crucial. Using caulk, weather stripping, and expanding foam can help to create a tight air barrier.
The *color* of the roofing material can also affect energy efficiency. Lighter-colored roofs reflect more sunlight, reducing heat gain in the summer. Darker-colored roofs absorb more sunlight, which can be beneficial in colder climates. The choice of roofing material should be based on the climate and the desired energy performance.
In addition, *radiant barriers* can be installed under the roof sheathing to reflect heat away from the attic space. Radiant barriers are particularly effective in hot climates, where they can significantly reduce cooling costs. These barriers typically consist of a thin layer of reflective material, such as aluminum foil, applied to a substrate.
By addressing these energy efficiency considerations during the design and construction phases, homeowners can enjoy the aesthetic benefits of vaulted ceilings without compromising energy performance. Careful planning and attention to detail are essential to creating a comfortable and energy-efficient living environment.

One Story House Plan With Vaulted Ceilings And Rear Grilling Porch 70582mk Architectural Designs Plans

Mountain Or Lake House Plan With Outdoor Fireplace And Vaulted Ceilings 92328mx Architectural Designs Plans

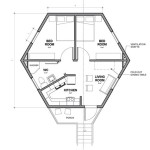
Small House Plan With Vaulted Ceiling All Bedroom Windows Directed In The Same Direction Floor Plans Building

Cathedral Ceiling House Plans Small W High Ceilings

One Level House Plan With Cathedral Ceilings In Living Room 860029mcd Architectural Designs Plans

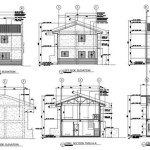
Appalachia Mountain A Frame Lake Or House Plan With Photos
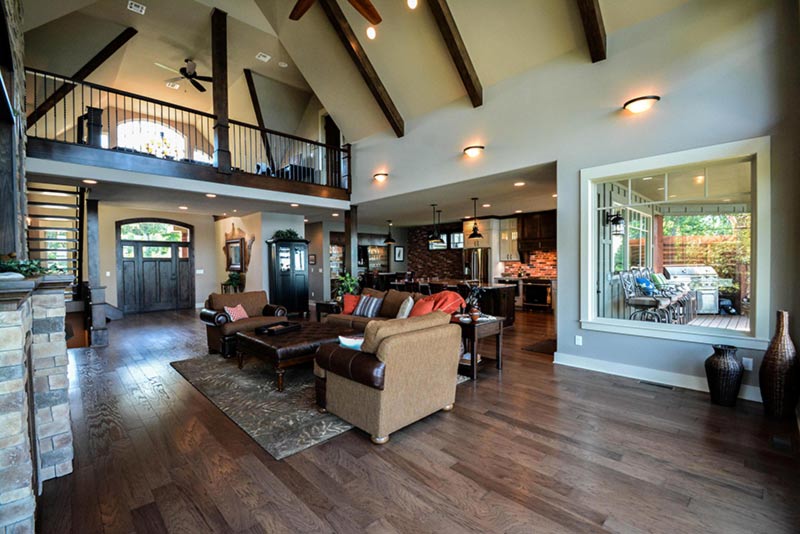

Rustic House Plans Our 10 Most Popular Home

Cathedral Ceiling House Plans Small W High Ceilings

Home Plans With Vaulted Or Volume Ceilings Find Floorplan

Exclusive Ranch House Plan With Cathedral Ceiling 440004pwl Architectural Designs Plans